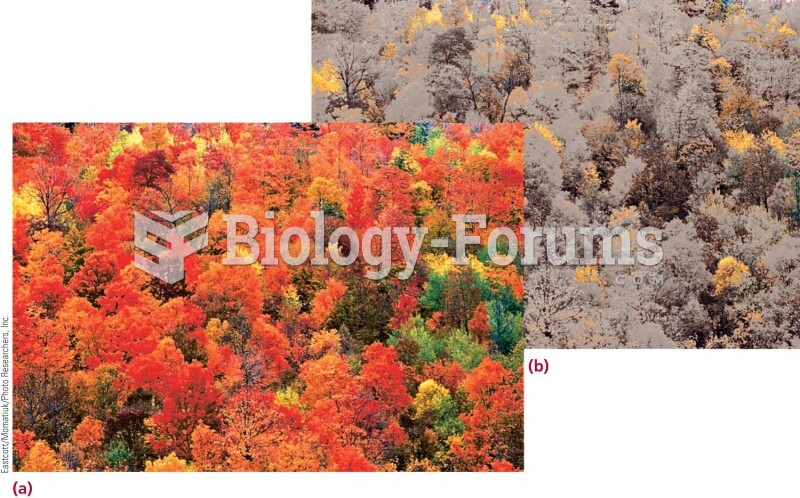
|
|
|
The lipid bilayer is made of phospholipids. They are arranged in a double layer because one of their ends is attracted to water while the other is repelled by water.
There are major differences in the metabolism of morphine and the illegal drug heroin. Morphine mostly produces its CNS effects through m-receptors, and at k- and d-receptors. Heroin has a slight affinity for opiate receptors. Most of its actions are due to metabolism to active metabolites (6-acetylmorphine, morphine, and morphine-6-glucuronide).
The B-complex vitamins and vitamin C are not stored in the body and must be replaced each day.
The familiar sounds of your heart are made by the heart's valves as they open and close.
Despite claims by manufacturers, the supplement known as Ginkgo biloba was shown in a study of more than 3,000 participants to be ineffective in reducing development of dementia and Alzheimer’s disease in older people.