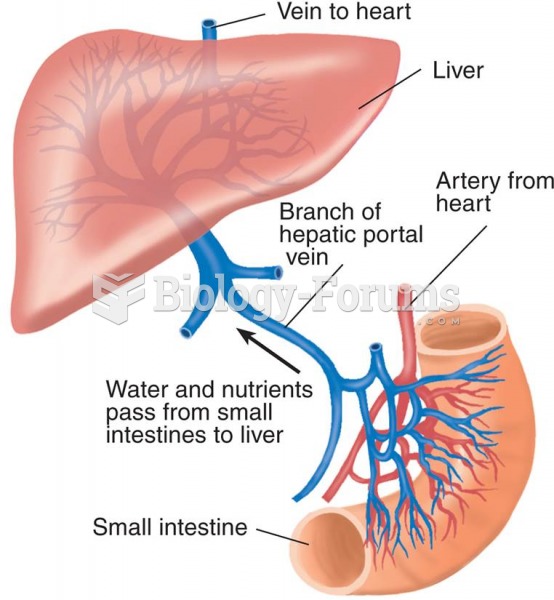
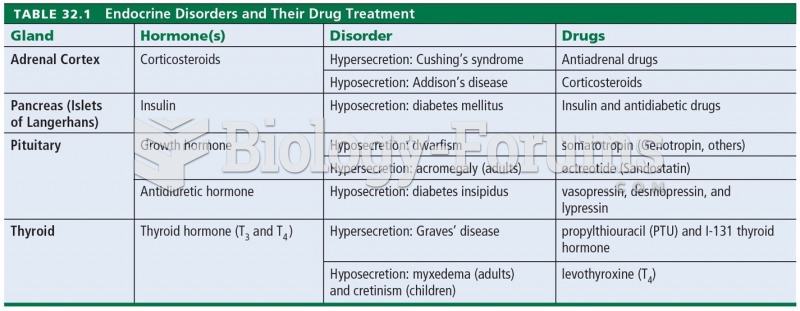
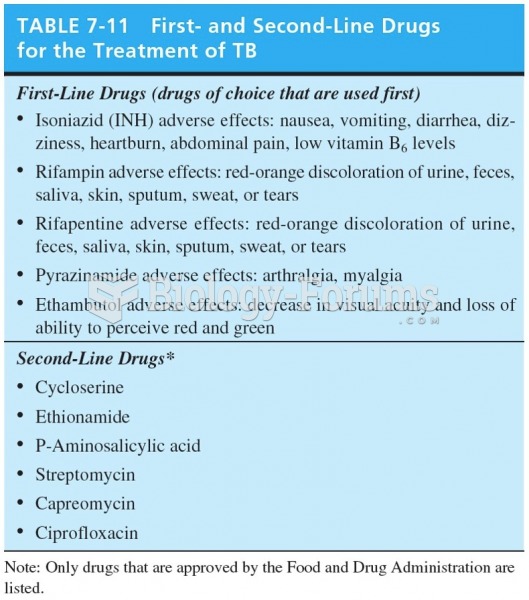
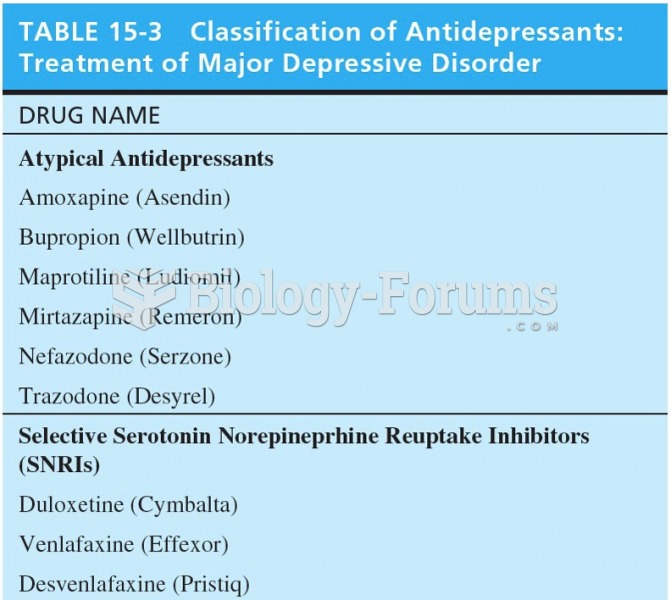
matching
a. Receives no treatment.
b. Participants are assigned to a group, treatment is administered, posttest is given.
c. Are not characterized by random selection of participants from a population, nor do they include a control group.
d. Selection of subjects for participation in a study.
e. The scoring of an instrument, such as a test.
f. Also called the Hawthorne effect, occurs when the subject of the study change because they are being studied, not because of any treatment.
g. An example of a true experimental design that does not include a pretest.
h. Quasi-experimental designs.
i. This tests for the presence of a distinct cause and effect.
j. The quality of an experimental design such that the results can be generalized from the original sample to another sample and then, by extension, to the population from which the sample originated.
k. The quality of an experimental design such that the results obtained are attributed to the manipulation of the independent variable.
l. Receives a treatment.
m. Another name for reactive arrangements
n. Factors that can decrease the internal validity of a study; variables that, if not accounted for can confound the results.
o. The tendency of scores to regress toward the mean rather than away from it.
p. Occurs when the presence or absence of a pretest changes the subjects' responses.
q. A statistical tool that equalizes any initial differences that might exist; it subtracts the influence of the relationship between the covariate and the dependent variable from the effect of one treatment.
r. A threat to internal validity that happens when those who drop out of a study change the nature of the sample.
s. An example of a true experimental design that involves an experimental group and three control groups, one of which actually receives the treatment as well.
t. Participants are assigned to a group, pretest is administered, treatment is administered, posttest is administered.
u. Changes caused by biological or psychological forces.
v. When subjects receive an unintended treatment in addition to the intended treatment.
w. A threat to internal validity that can happen when a pretest affects performance on later measures, such as a posttest.
x. Actions of the experimenter that have an impact on the experiment.
y. For every occurrence of an individual with a score of X in the experimental group, the researcher would make sure there is a person in the control group with a similar score.
z. Events can occur outside of the experiment that may affect its outcome.
zz. An example of a true experimental design.
1. True experimental research method
2. Experimental group
3. Control group
4. Causal-comparative designs
5. Pre-experimental designs
6. One-shot case study design
7. One-group pretest posttest design
8. Pretest posttest control group design
9. Posttest-only control group design
10. Solomon four-group design
11. Internal validity
12. External validity
13. History
14. Maturation
15. Selection
16. Testing
17. Instrumentation
18. Regression
19. Mortality (or attrition)
20. Multiple treatment interference
21. Reactive arrangements
22. Hawthorne effect
23. Experimenter effects
24. Pretest sensitization
25. Extraneous variables
26. Matching
27. Analysis of covariance
Question 2
Advantages to within subject designs include fewer participants, less statistical variance, and equal group sizes.
Indicate whether the statement is true or false