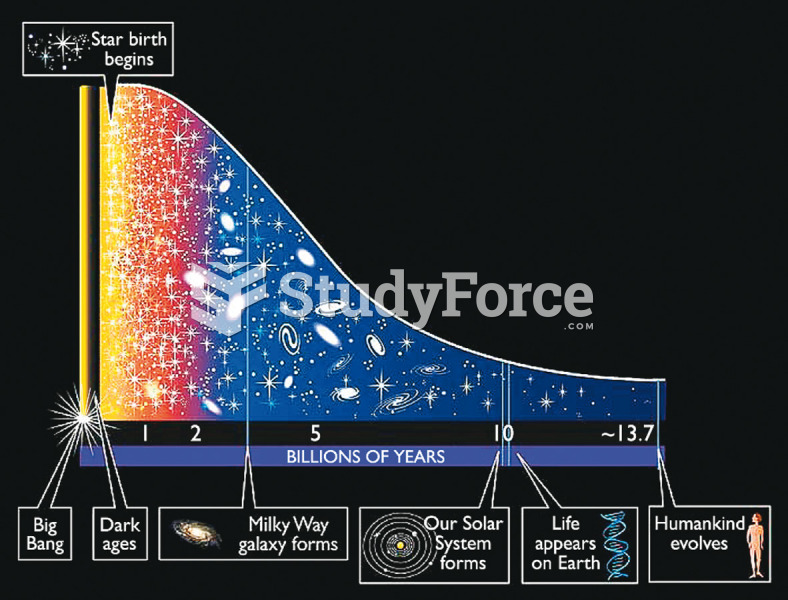
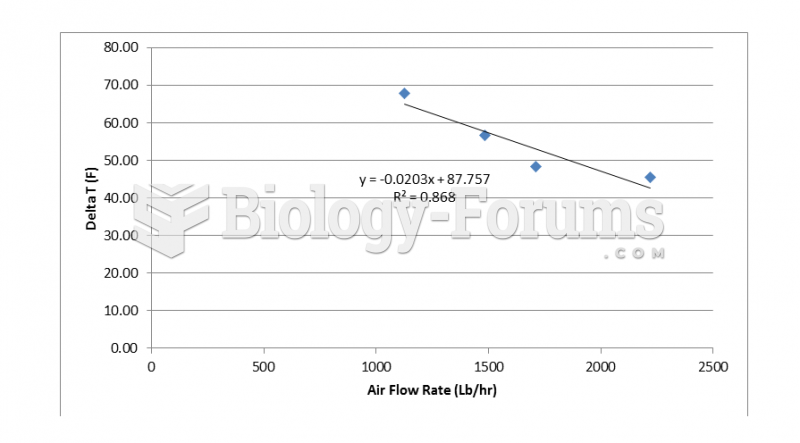
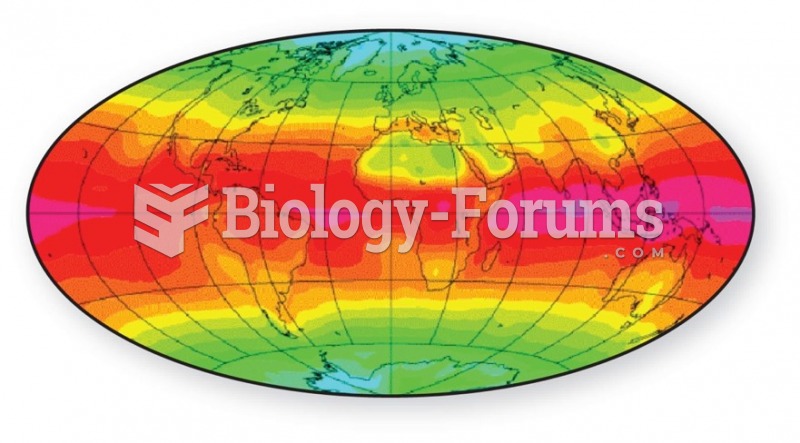
Answer to Question 1
ANSWER: If a parcel of air expands and cools, or compresses and warms, with no interchange of heat with its surroundings, this situation is called an adiabatic process. As long as the air in the parcel is unsaturated (the relative humidity is less than 100 percent), the rate of adiabatic cooling or warming remains constant. This rate of heating or cooling is about 10 degrees Celsius for every 1000 m of change in elevation (5.5 degrees Fahrenheit per 1000 ft). Because this rate applies only to unsaturated air, it is called the dry adiabatic rate. As the rising air cools, its relative humidity increases as the air temperature approaches the dew-point temperature. If the rising air cools to its dew-point temperature, the relative humidity becomes 100 percent. Further lifting results in condensation; a cloud forms, and latent heat is released inside the rising air parcel. Because the heat added during condensation offsets some of the cooling due to expansion, the air no longer cools at the dry adiabatic rate but at a lesser rate called the moist adiabatic rate. If a saturated parcel containing water droplets were to sink, it would compress and warm at the moist adiabatic rate because evaporation of the liquid droplets would offset the rate of compressional warming. Hence, the rate at which rising or sinking saturated air changes temperaturethe moist adiabatic rateis less than the dry adiabatic rate.
Answer to Question 2
ANSWER: Surface heating and free convection: Air in contact with the warm surface becomes warmer than its surroundings and rises. Example: cumulus cloud. Topography: Horizontally moving air forced to rise over a mountain range. Example: orographic clouds, which form on the upwind side of the range. Widespread ascent: Rising air due to convergence in low pressure systems. Example: stratocumulus and nimbostratus. Uplift along weather fronts: fronts lift the air, causing adiabatic cooling, condensation and clouds. Example: cumulonimbus clouds in the vicinity of a cold front.