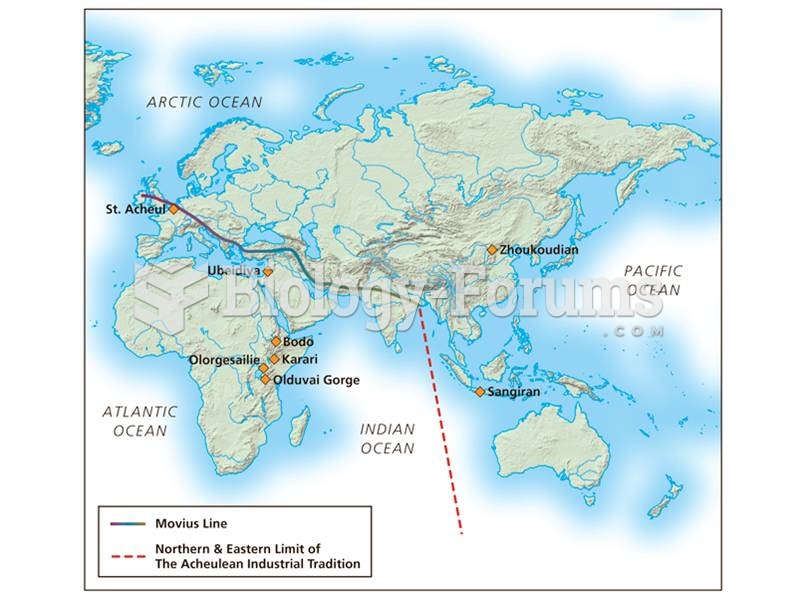
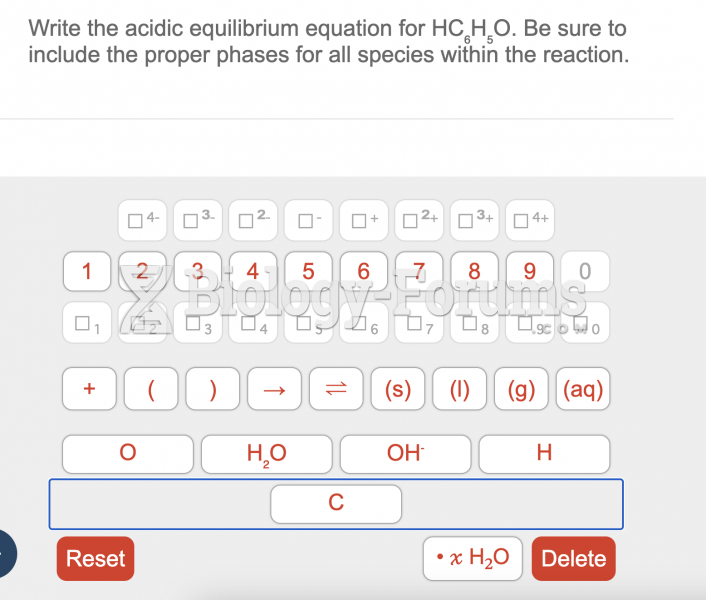
This topic contains a solution. Click here to go to the answer
|
|
|
Did you know?
Bacteria have flourished on the earth for over three billion years. They were the first life forms on the planet.
Did you know?
On average, someone in the United States has a stroke about every 40 seconds. This is about 795,000 people per year.
Did you know?
No drugs are available to relieve parathyroid disease. Parathyroid disease is caused by a parathyroid tumor, and it needs to be removed by surgery.
Did you know?
The people with the highest levels of LDL are Mexican American males and non-Hispanic black females.
Did you know?
About 3.2 billion people, nearly half the world population, are at risk for malaria. In 2015, there are about 214 million malaria cases and an estimated 438,000 malaria deaths.