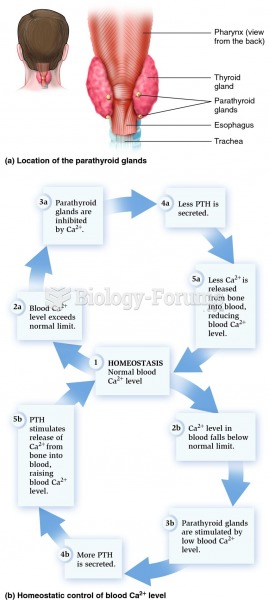
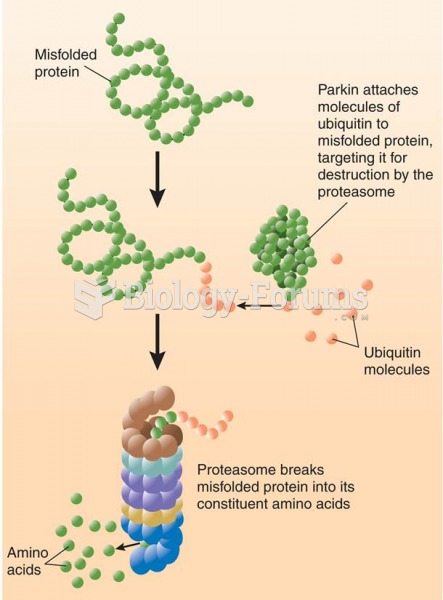
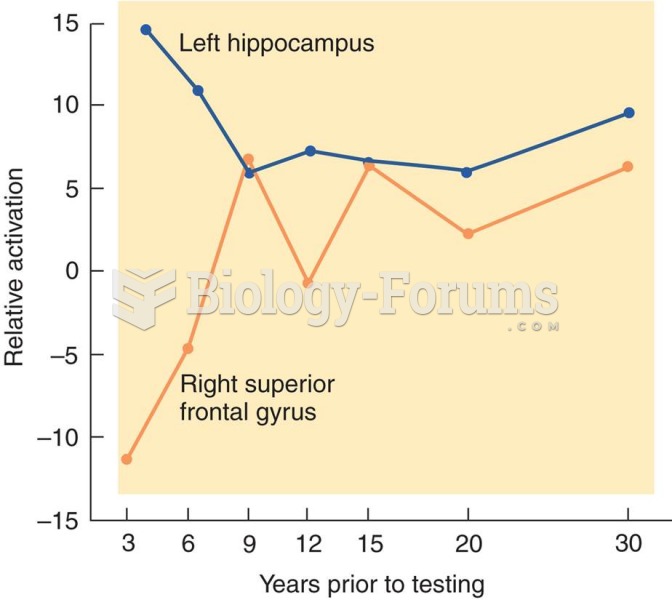
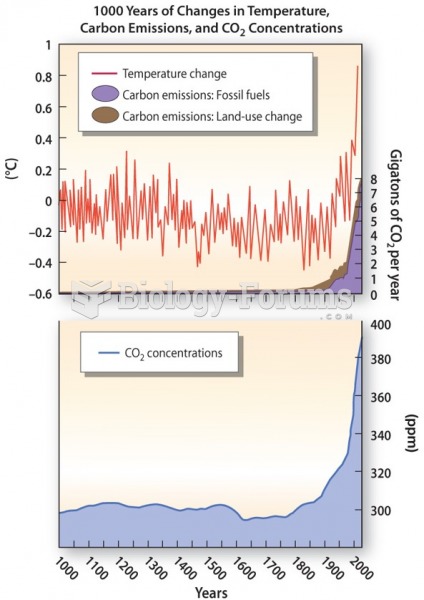
Answer to Question 1
Answer: By some accounts, tourism is the world's largest industry, with international tourist receipts exceeding 900 billion in 2010. Tourists spend large sums of money in their destinations on everything from hotels and meals to recreation, souvenirs and taxes. In most countries, tourism is one of the fastest-growing sectors of the economy and is a ignicant income source for many poor countries. For example, tourism receipts equal about 14 percent of Cambodia's GNI and about 7.5 of Egypt's GNI.
Many poor countries are pursuing economic development strategies that exploit areas of natural beauty. Unfortunately, these are oen areas in which additional visitors may harm the natural environment. Tourists require hotels, transportation, and food that take up land, create pollution, and draw on food supplies. Tourists use up scarce potable water suppliesespecially in luxury hotels, swimming pools, and laundry services. This puts pressure on local natural areas. The problems are not limited to developing countries dependent on tourism. Resort areas in Europe's Mediterranean put an enormous strain on scarce fresh water supplies while dumping large amounts of wastewater into sensitive watersheds.
The number of international tourists has more than doubled during the last two decades., reaching about 940 million in 2010. Half of the world's international tourist head to Europe. China, Turkey, Malaysia,and Mexico are also among the most popular destinations. Europeans and Asians are similarly the main source of international tourists
Answer to Question 2
Answer: Interregional migration is the relative long-distance movement from one region of a country to another. The most famous example of interregional migration is the opening the American west. Two hundred years ago, the United States consisted of a collection of settlements concentrated on the Atlantic Coast. Through mass interregional migration, the rest of the continent was settled and developed.
Intraregional migration is movement constrained to within the same region. Intraregional migration is much more common than interregional or international migration. Most intraregional migration has been from rural to urban areas or from cities to suburbs.