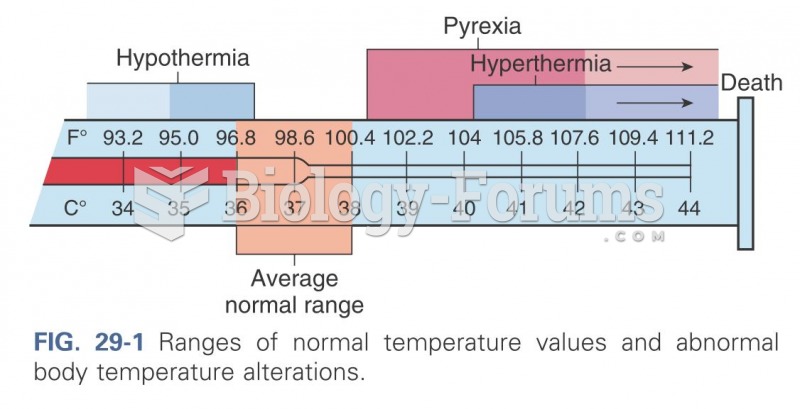
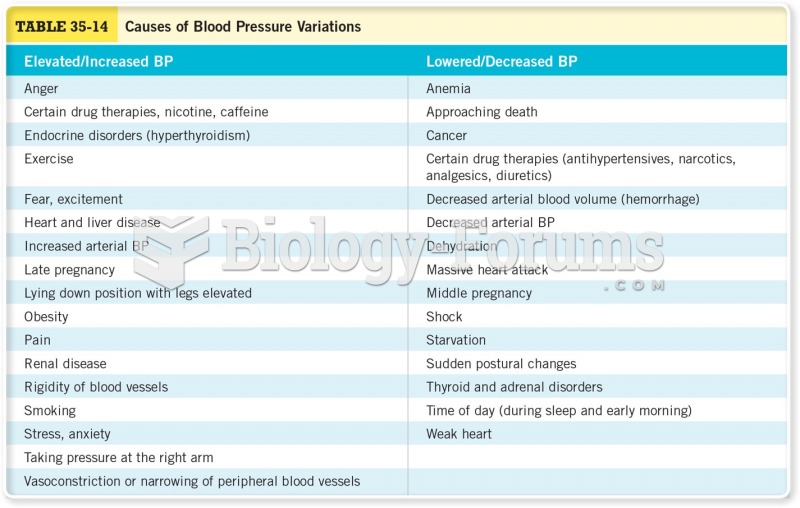
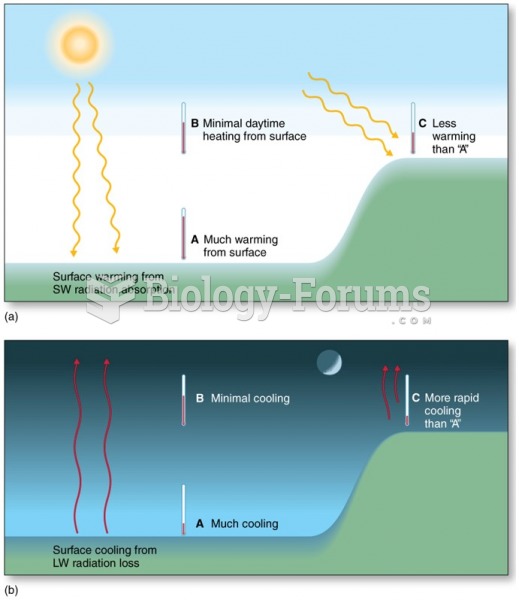
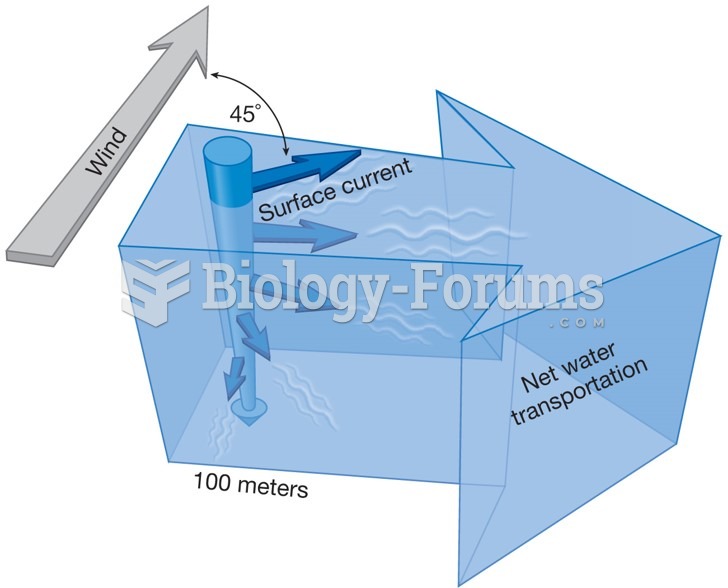
Answer to Question 1
Answer: The most important factor influencing the temperature of the Earth's surface is energy input, in the form of radiation from the Sun The amount of heat stored in water and proximity to the oceans also affects temperature. Generally, low latitudes have higher temperatures and continental locations have larger ranges of temperature.
First, on average, the highest temperatures are found in low latitudes, because the Sun is highest in the sky in these areas, and therefore the intensity of solar radiation is highest. High solar elevation angles occur throughout the year, and this makes the tropics consistently warm.
Secondly, continental interiors have larger temperature ranges. Large landmasses in high latitudes, such as North America and Asia have very large temperature differences between January and July, sometimes as high as 90 degrees. In contrast, the temperatures differences between June and January in the Aleutian Islands of the north Pacific, at about the same latitude as Siberia, is only about 18F. The climates of areas near the ocean compared with the climatic extremes of middle of continental regions are a result of this heat storage in water, and the advection of heat from ocean areas to adjacent land areas.
Answer to Question 2
Answer: Convection is movement in a fluid, caused when part of the fluid (whether gas or liquid) is heated. The heated portion expands and becomes less dense, rising up through the cooler portion. It causes the turbulence in water and in puffy white clouds overhead. In becoming less dense, meaning weighing less per unit of volume, warm air rises above cooler, denser air, just as a hot-air balloon rises through the cooler air surrounding it. Convection is caused by heating the atmosphere from below. Temperature changes resulting from vertical motions create clouds and precipitation
When air rises, it has less weight above it, and the lower pressure allows the air to expand. The expansion leads to a decrease in temperature. The decrease in temperature that results is called adiabatic cooling. When convection causes air to rise, the pressure in that air decreases with elevation and this causes the air to cool. Cooling, in turn, lowers the amount of water vapor it can hold.
Condensation occurs when the amount of water the air can hold reaches the actual vapor content, that is the relative humidity reaches 100. Above the condensation level, rising air continues to cool, further reducing its ability to hold water vapor leading to more condensation. This releases latent heat, warming than air. The added heat isn't enough to prevent condensation, but it does make the air warmer that the air around it at the same elevation, and so promotes further rising air.