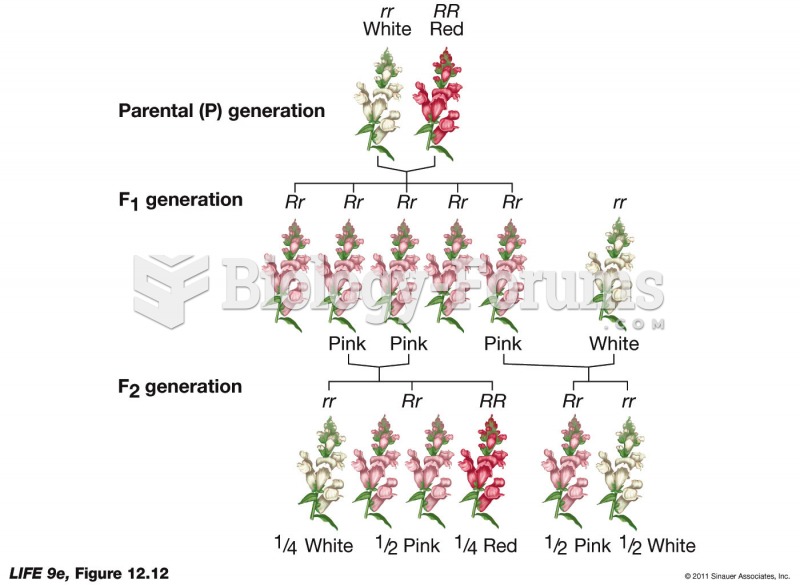
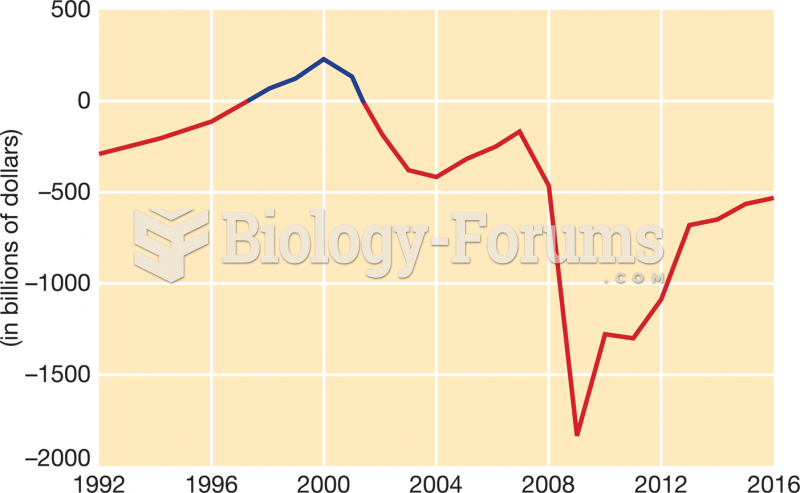
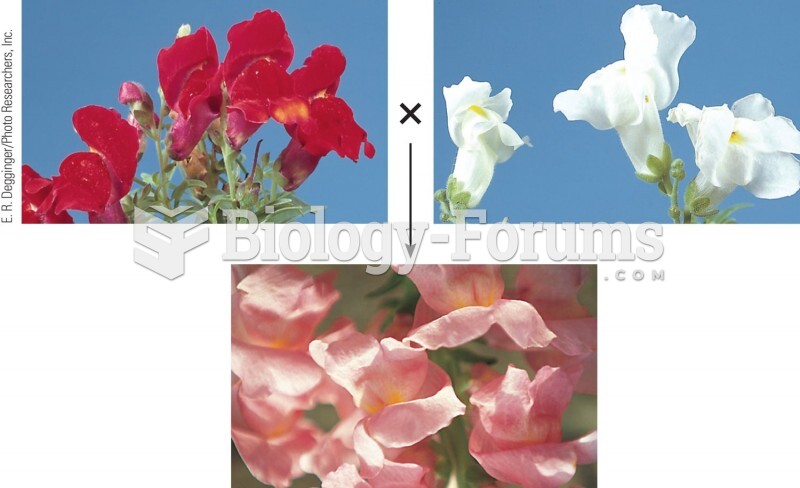
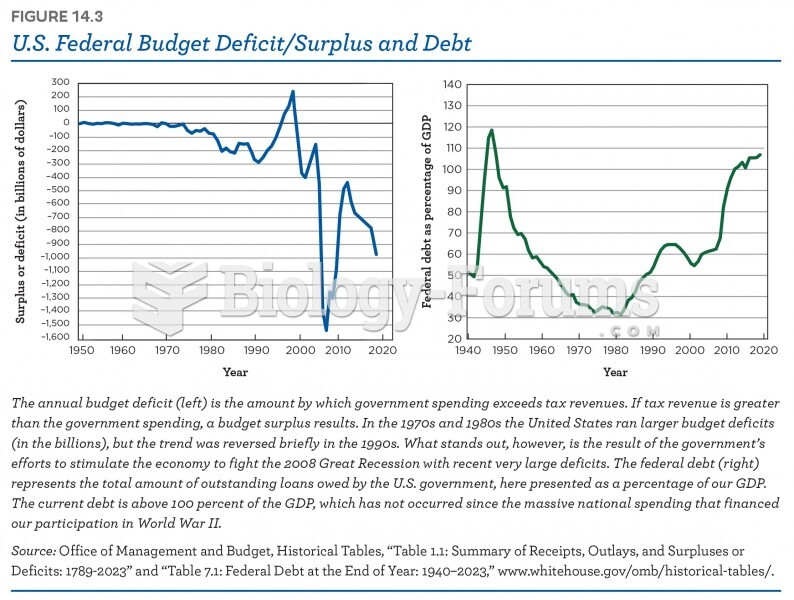
|
|
|
Everyone has one nostril that is larger than the other.
A cataract is a clouding of the eyes' natural lens. As we age, some clouding of the lens may occur. The first sign of a cataract is usually blurry vision. Although glasses and other visual aids may at first help a person with cataracts, surgery may become inevitable. Cataract surgery is very successful in restoring vision, and it is the most frequently performed surgery in the United States.
Eat fiber! A diet high in fiber can help lower cholesterol levels by as much as 10%.
It is widely believed that giving a daily oral dose of aspirin to heart attack patients improves their chances of survival because the aspirin blocks the formation of new blood clots.
The average office desk has 400 times more bacteria on it than a toilet.