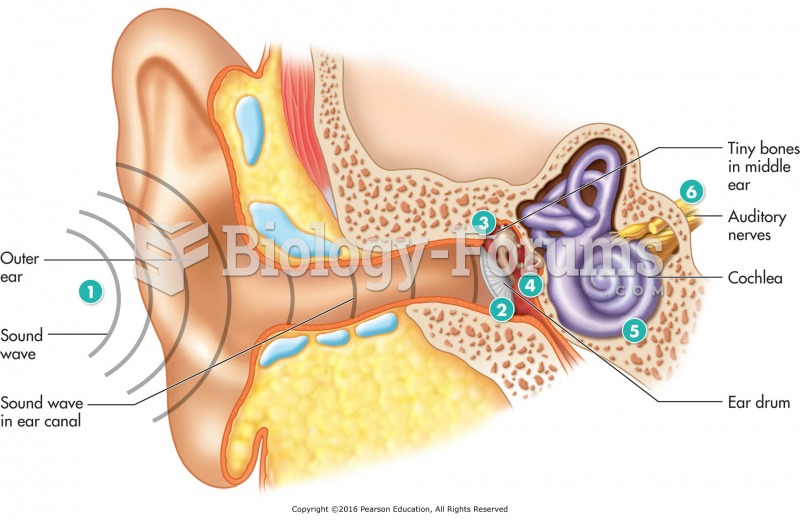
|
|
|
Inotropic therapy does not have a role in the treatment of most heart failure patients. These drugs can make patients feel and function better but usually do not lengthen the predicted length of their lives.
One way to reduce acid reflux is to lose two or three pounds. Most people lose weight in the belly area first when they increase exercise, meaning that heartburn can be reduced quickly by this method.
By definition, when a medication is administered intravenously, its bioavailability is 100%.
The cure for trichomoniasis is easy as long as the patient does not drink alcoholic beverages for 24 hours. Just a single dose of medication is needed to rid the body of the disease. However, without proper precautions, an individual may contract the disease repeatedly. In fact, most people develop trichomoniasis again within three months of their last treatment.
The people with the highest levels of LDL are Mexican American males and non-Hispanic black females.