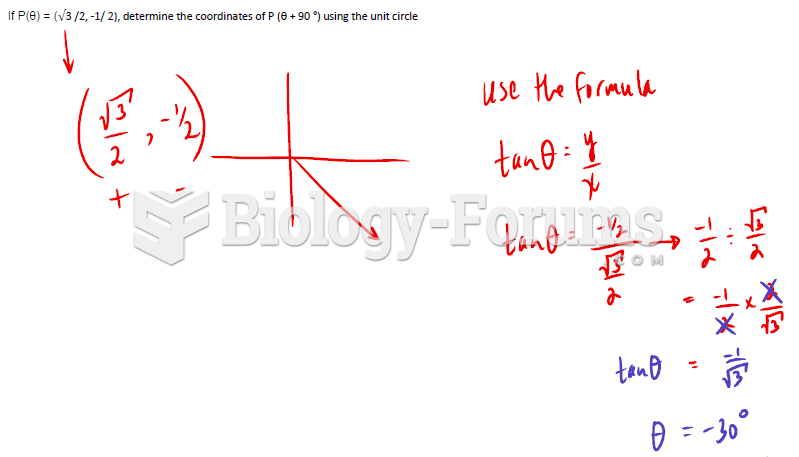
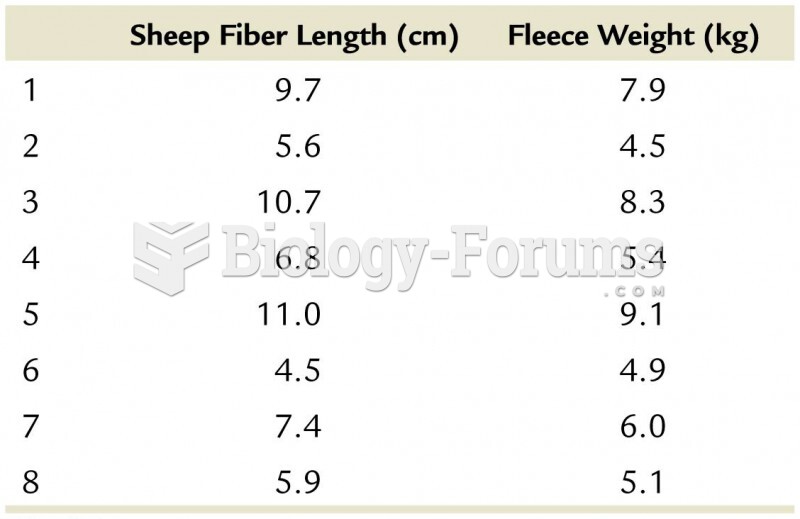
|
|
|
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus or MRSA was discovered in 1961 in the United Kingdom. It if often referred to as a superbug. MRSA infections cause more deaths in the United States every year than AIDS.
Persons who overdose with cardiac glycosides have a better chance of overall survival if they can survive the first 24 hours after the overdose.
Your skin wrinkles if you stay in the bathtub a long time because the outermost layer of skin (which consists of dead keratin) swells when it absorbs water. It is tightly attached to the skin below it, so it compensates for the increased area by wrinkling. This happens to the hands and feet because they have the thickest layer of dead keratin cells.
More than 20 million Americans cite use of marijuana within the past 30 days, according to the National Survey on Drug Use and Health (NSDUH). More than 8 million admit to using it almost every day.
The largest baby ever born weighed more than 23 pounds but died just 11 hours after his birth in 1879. The largest surviving baby was born in October 2009 in Sumatra, Indonesia, and weighed an astounding 19.2 pounds at birth.