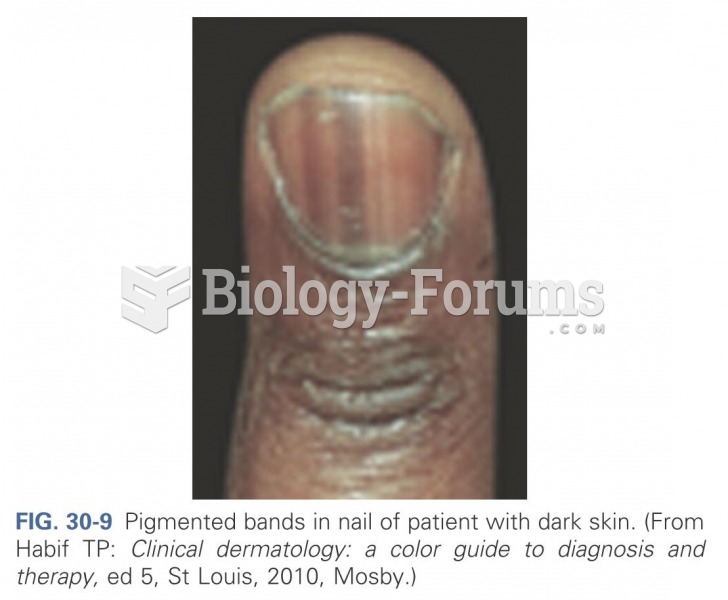
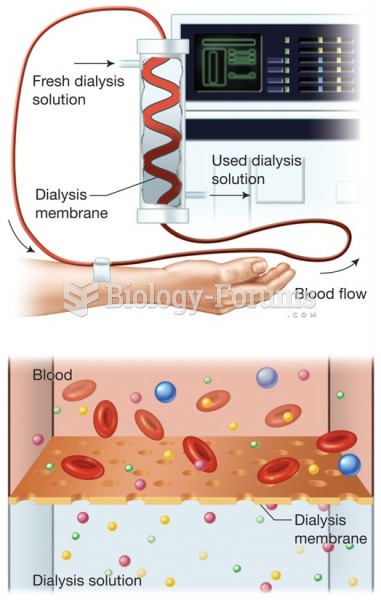
|
|
|
A recent study has found that following a diet rich in berries may slow down the aging process of the brain. This diet apparently helps to keep dopamine levels much higher than are seen in normal individuals who do not eat berries as a regular part of their diet as they enter their later years.
Pink eye is a term that refers to conjunctivitis, which is inflammation of the thin, clear membrane (conjunctiva) over the white part of the eye (sclera). It may be triggered by a virus, bacteria, or foreign body in the eye. Antibiotic eye drops alleviate bacterial conjunctivitis, and antihistamine allergy pills or eye drops help control allergic conjunctivitis symptoms.
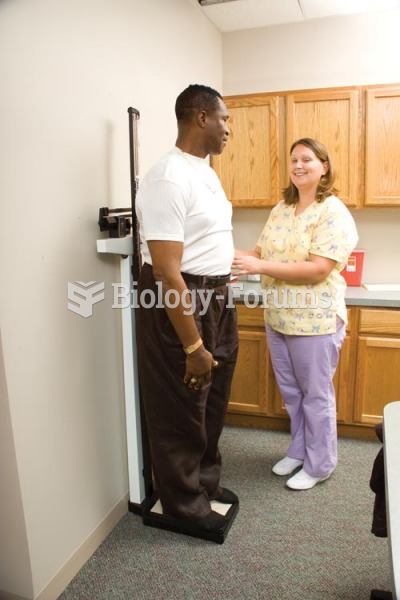
The top 10 most important tips that will help you grow old gracefully include (1) quit smoking, (2) keep your weight down, (3) take supplements, (4) skip a meal each day or fast 1 day per week, (5) get a pet, (6) get medical help for chronic pain, (7) walk regularly, (8) reduce arguments, (9) put live plants in your living space, and (10) do some weight training.
Blood is approximately twice as thick as water because of the cells and other components found in it.
Blastomycosis is often misdiagnosed, resulting in tragic outcomes. It is caused by a fungus living in moist soil, in wooded areas of the United States and Canada. If inhaled, the fungus can cause mild breathing problems that may worsen and cause serious illness and even death.