Answer to Question 1
ANS: C
A. Incorrect response: See explanation C.
B. Incorrect response: See explanation C.
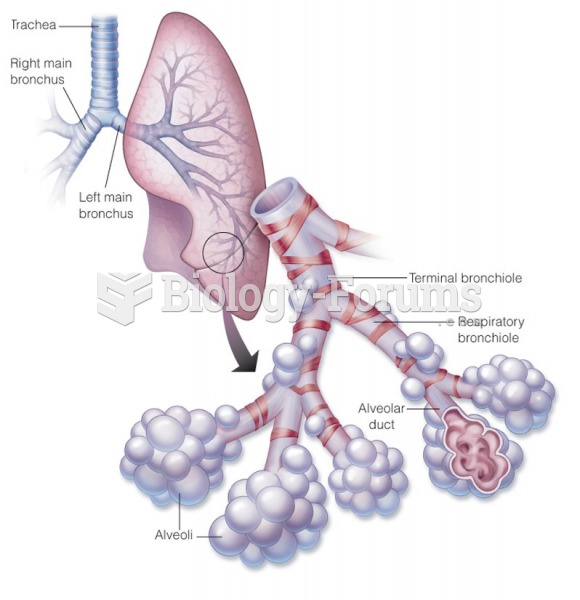
C. Correct response: In overdistended alveoli produced by excessively applied positive pressure, the pressure-volume relationships become flattened. Furthermore, because both ventilation and perfusion decrease in overdistended regions, ventilationperfusio n relationships fluctuate. Overdistention can also cause ventilator-induced lung damage, alveolar rupture, and biotrauma.
D. Incorrect response: See explanation C.
Answer to Question 2
ANS: D
A. Incorrect response: Capillary shunting affects the patient's PaO2 more than it does the PaCO2. If a patient has enough normal alveoli, along with alveoli exhibiting capillary shunting, the normal alveoli can become high ventilationperfusio n units and compensate for the PaCO2, but not for the PaO2. The nonlinear relationship between the PaO2 and the O2 content (O2 attached to hemoglobin) prohibits this type of compensation for oxygenation of the patient's plasma.
B. Incorrect response: Capillary shunting does not cause wasted ventilation (i.e., alveolar dead space).
C. Incorrect response: When capillary shunting exists, most of the ventilation does not preferentially enter the apical alveoli.
D. Correct response: Capillary shunting defines alveoli that are not ventilated, but perfused. Alveolar perfusion does not participate in gas exchange in alveoli experiencing capillary shunting. The nonlinear relationship between the PaO2 and oxyhemoglobin does not permit the hyperventilation of normal alveoli to compensate for the decreased PaO2. Such hyperventilation compensates for the PCO2 because of the linear relationship between alveolar ventilation and the PaCO2. As alveolar ventilation increases while CO2 production remains constant, the PaCO2 decreases.