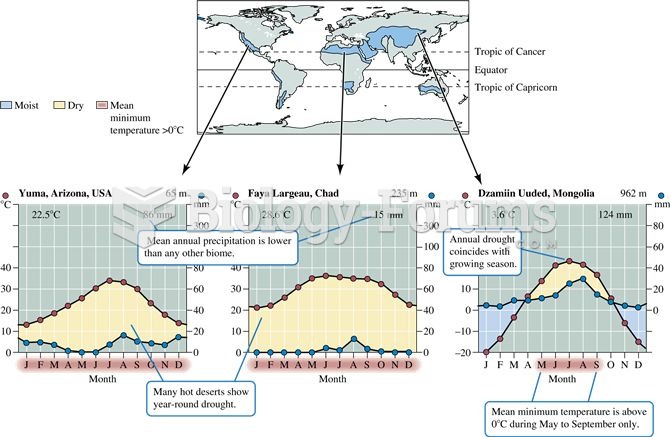
|
|
|
Certain chemicals, after ingestion, can be converted by the body into cyanide. Most of these chemicals have been removed from the market, but some old nail polish remover, solvents, and plastics manufacturing solutions can contain these substances.
A strange skin disease referred to as Morgellons has occurred in the southern United States and in California. Symptoms include slowly healing sores, joint pain, persistent fatigue, and a sensation of things crawling through the skin. Another symptom is strange-looking, threadlike extrusions coming out of the skin.
Increased intake of vitamin D has been shown to reduce fractures up to 25% in older people.
Multiple sclerosis is a condition wherein the body's nervous system is weakened by an autoimmune reaction that attacks the myelin sheaths of neurons.
The calories found in one piece of cherry cheesecake could light a 60-watt light bulb for 1.5 hours.