|
|
|
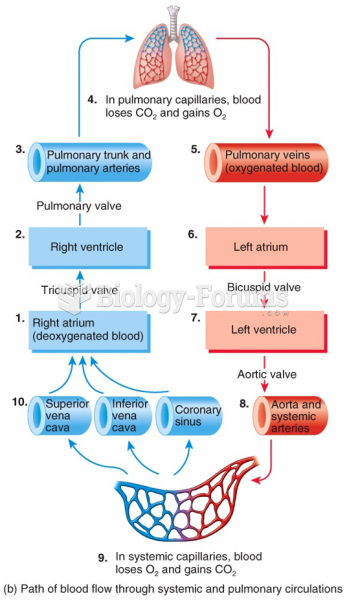
Congestive heart failure is a serious disorder that carries a reduced life expectancy. Heart failure is usually a chronic illness, and it may worsen with infection or other physical stressors.
The effects of organophosphate poisoning are referred to by using the abbreviations “SLUD” or “SLUDGE,” It stands for: salivation, lacrimation, urination, defecation, GI upset, and emesis.
Never take aspirin without food because it is likely to irritate your stomach. Never give aspirin to children under age 12. Overdoses of aspirin have the potential to cause deafness.
Elderly adults are at greatest risk of stroke and myocardial infarction and have the most to gain from prophylaxis. Patients ages 60 to 80 years with blood pressures above 160/90 mm Hg should benefit from antihypertensive treatment.
The strongest synthetic topical retinoid drug available, tazarotene, is used to treat sun-damaged skin, acne, and psoriasis.