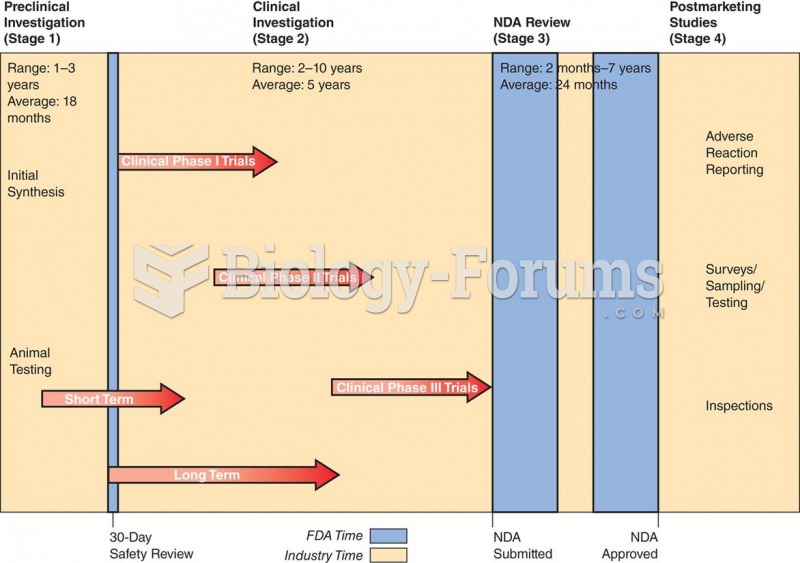
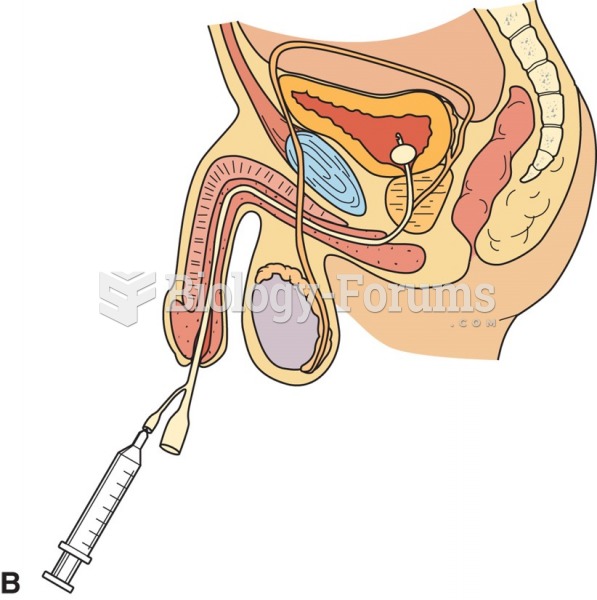
This topic contains a solution. Click here to go to the answer
|
|
|
Did you know?
For high blood pressure (hypertension), a new class of drug, called a vasopeptidase blocker (inhibitor), has been developed. It decreases blood pressure by simultaneously dilating the peripheral arteries and increasing the body's loss of salt.
Did you know?
More than 34,000 trademarked medication names and more than 10,000 generic medication names are in use in the United States.
Did you know?
Between 1999 and 2012, American adults with high total cholesterol decreased from 18.3% to 12.9%
Did you know?
Most women experience menopause in their 50s. However, in 1994, an Italian woman gave birth to a baby boy when she was 61 years old.
Did you know?
The first oncogene was discovered in 1970 and was termed SRC (pronounced "SARK").