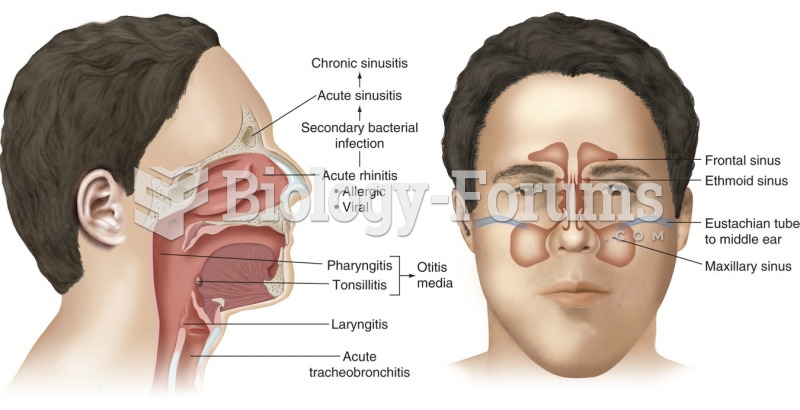
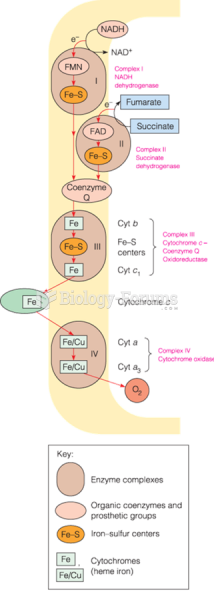
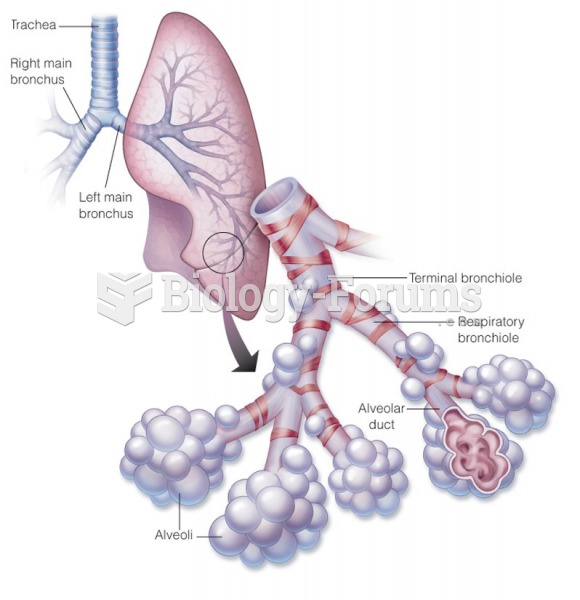
|
|
|
Each year in the United States, there are approximately six million pregnancies. This means that at any one time, about 4% of women in the United States are pregnant.
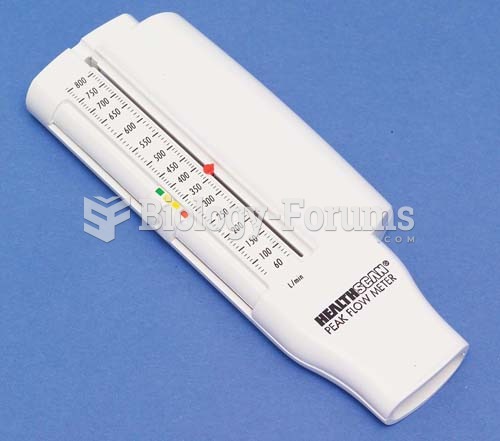
Serum cholesterol testing in adults is recommended every 1 to 5 years. People with diabetes and a family history of high cholesterol should be tested even more frequently.
The heart is located in the center of the chest, with part of it tipped slightly so that it taps against the left side of the chest.
According to the American College of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology, more than 50 million Americans have some kind of food allergy. Food allergies affect between 4 and 6% of children, and 4% of adults, according to the CDC. The most common food allergies include shellfish, peanuts, walnuts, fish, eggs, milk, and soy.
Approximately one in four people diagnosed with diabetes will develop foot problems. Of these, about one-third will require lower extremity amputation.
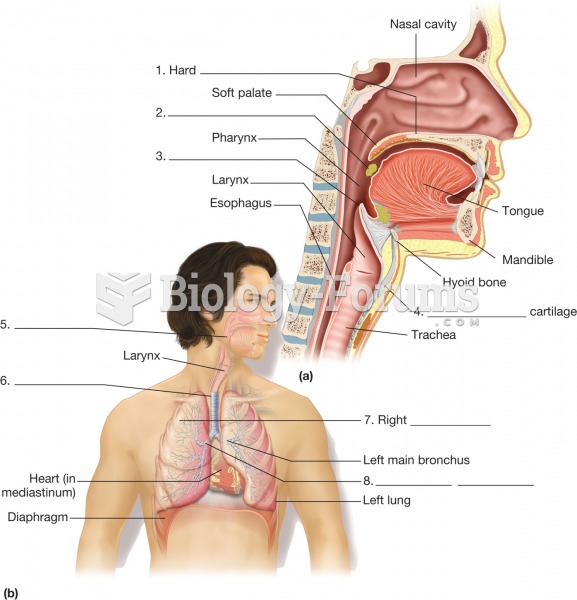 The respiratory system. (a) Sagittal section of the head and neck, revealing the organs of the upper
The respiratory system. (a) Sagittal section of the head and neck, revealing the organs of the upper
 Each of the eight injectors shown are producing a correct spray pattern for the applications. While ...
Each of the eight injectors shown are producing a correct spray pattern for the applications. While ...