|
|
|
In 1835 it was discovered that a disease of silkworms known as muscardine could be transferred from one silkworm to another, and was caused by a fungus.
Many people have small pouches in their colons that bulge outward through weak spots. Each pouch is called a diverticulum. About 10% of Americans older than age 40 years have diverticulosis, which, when the pouches become infected or inflamed, is called diverticulitis. The main cause of diverticular disease is a low-fiber diet.
Fewer than 10% of babies are born on their exact due dates, 50% are born within 1 week of the due date, and 90% are born within 2 weeks of the date.
Computer programs are available that crosscheck a new drug's possible trade name with all other trade names currently available. These programs detect dangerous similarities between names and alert the manufacturer of the drug.
In ancient Rome, many of the richer people in the population had lead-induced gout. The reason for this is unclear. Lead poisoning has also been linked to madness.
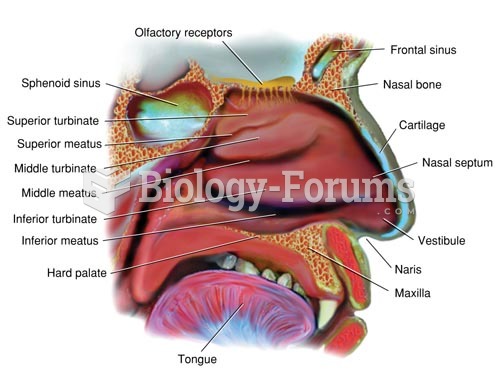
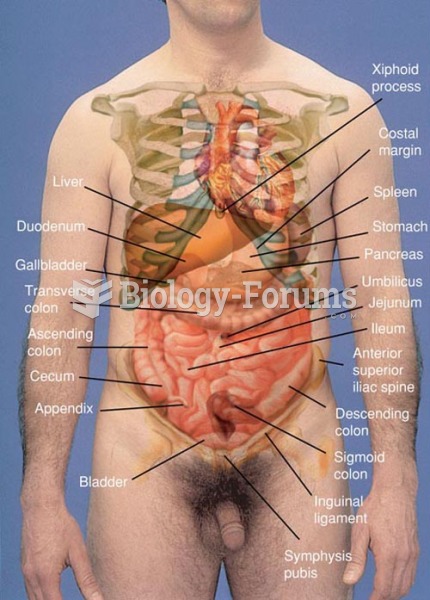
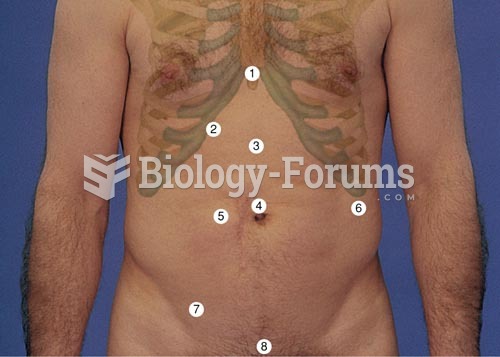 Abdominal Assessment Landmarks. When describing pathology of the abdomen, it is useful to use theses
Abdominal Assessment Landmarks. When describing pathology of the abdomen, it is useful to use theses
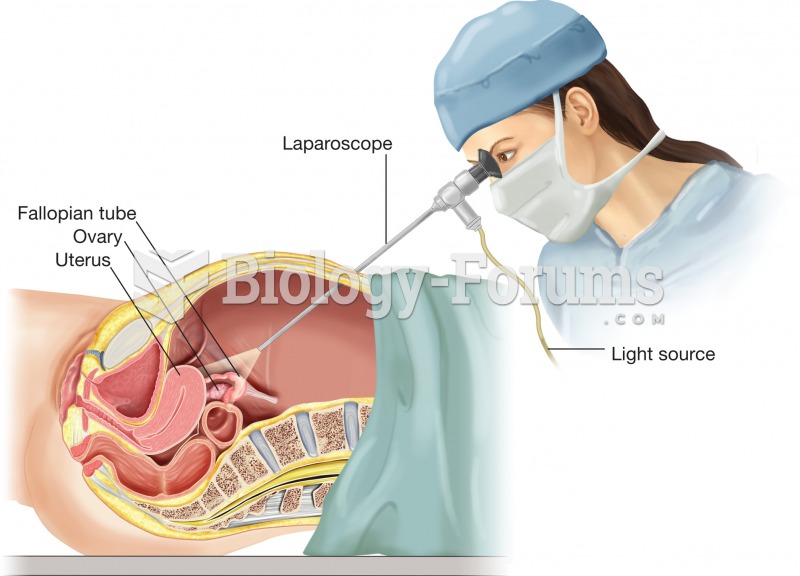 Laparoscopy. A lighted endoscope specialized for insertion into the abdomen, called a laparoscope, i
Laparoscopy. A lighted endoscope specialized for insertion into the abdomen, called a laparoscope, i