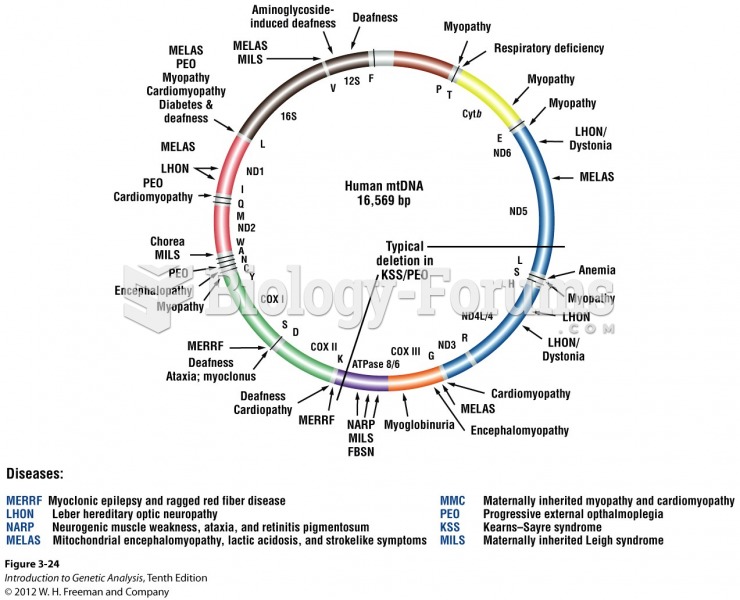
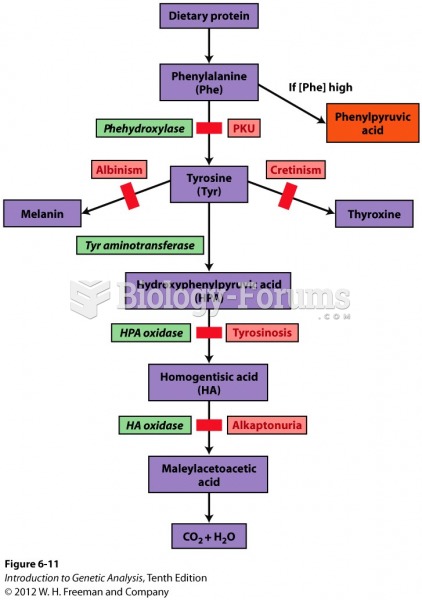
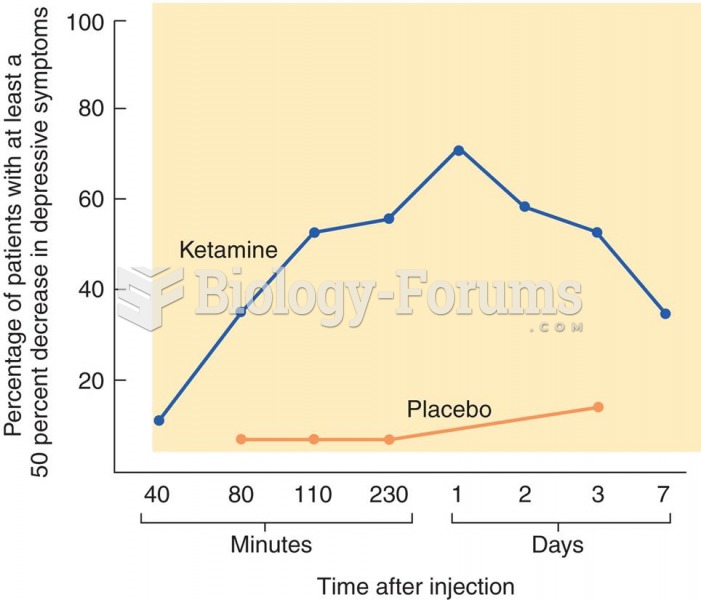
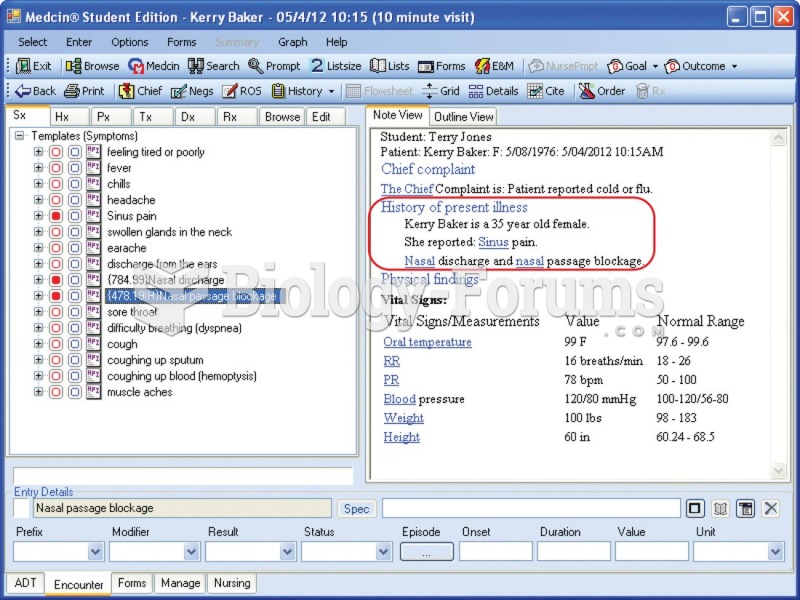
Answer to Question 1
Feline panleukopeniaCats usually show signs of depression, loss of appetite, high fever, lethargy,
vomiting, dehydration, and hanging over the waster dish. Diarrhea may show large amount of liquid,
mucus, and blood.
Feline herpes virus and feline calicivirusEarly signs of infection are depression, sneezing, and coughing.
As the infection progresses, severe eye and nasal discharges occur, with an increase in temperature.
Feline rhinotracheitisThis disease is characterized by sneezing and discharges from the eyes and nasal
passages.
Feline infectious peritonitisThere are two forms of this disease. In one form, the abdomen and chest
accumulate fluid. The cat experiences a fever, refuses to eat, appears depressed, and loses weight. As the disease
progresses, the body cavities continue to fill with fluid; organ systems are affected; and signs of specific organ
failure occur. Death may eventually occur as a result of organ failure. The second form is usually associated
with specific organ failure. Lesions affecting the cat's eyes are very common and may be the first indication of
the disease. In this form, the disease may progress to the point that the cat dies from organ failure.
Feline leukemia virus (FeLV)Early symptoms of the disease may include fever, swollen lymph nodes,
weakness, jaundice, weight loss, listlessness, and lethargy.
Feline pneumonitisRunny eyes and nose are symptoms of this disease.
RabiesSudden loss of appetite, signs of apprehension or nervousness, irritability, and hyper-excitability
are symptoms of rabies. The animal may seek solitude, or an otherwise unfriendly animal may become
friendly. Uncharacteristic aggressiveness can develop, and wild animals may lose their fear of people.
Animals that are normally nocturnal may be seen wandering around during the daytime. The animal may
become irritable and may viciously and aggressively use its teeth and claws.
Feline urologic syndromeSymptoms of this syndrome range from mild inflammation to a blockage of the
uretha, uremic poisoning, and death.
Wet eyesThis is a condition of excessive tear production or blockage of the canals that normally drain
tears into the nasal cavity, causing tears to overflow at the inner corners of the eyes.
ToxoplasmosisInfect ed cats may develop fever, an abnormal yellowing of the skin, tissues, eyes,
and urine known as jaundice, enlarged lymph nodes, difficulty breathing, anemia, eye inflammation,
encephalitis, and intestinal disease. Abortion is also seen in pregnant cats that are infected. Cats may
develop stiff, painful muscles and have difficulty moving or be unable to move.
Ascarids and hookwormsSymptoms are basically the same as in dogs. Symptoms may not occur in cats
because cats do not become as heavily infected as dogs.
TapewormsTapeworms do not cause major harm to cats. The tapeworms consume nutrients from the cat
and deprive the cat of needed nutrients. Infected cats will usually lose weight and have a rough hair coat.
Lice (Felicola subrostratus)Healthy and well-cared-for cats are unlikely to be troubled by lice. When a cat
is infected, the lice are usually found around the head.
Mites (Demodes cati)Patchy hair loss, reddening, and occasionally crusting on the neck, ears, and head
are signs of mites. Severe cases may involve the entire body.
Feline scabies or notoedric mange (caused by Notoedres cati)This skin disease causes hair loss and
thickening and crusting of the skin, usually affecting the head and forelegs.
Answer to Question 2
Contagious diseases
Noncontagious diseases
Internal parasites
External parasites
Fungal diseases
Poisonings