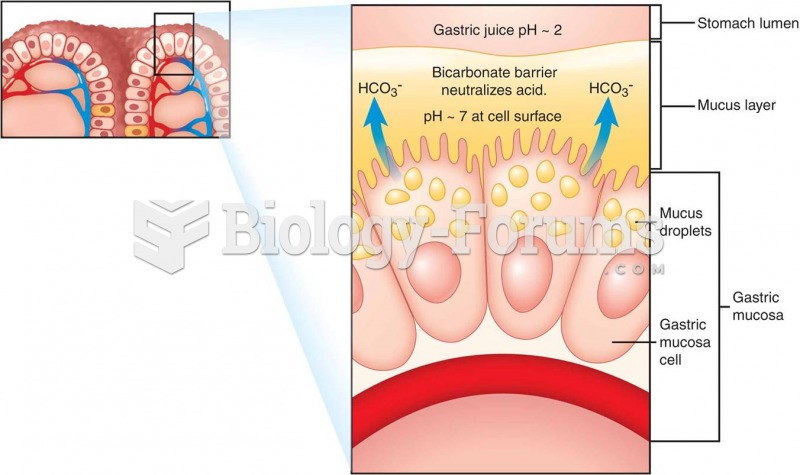
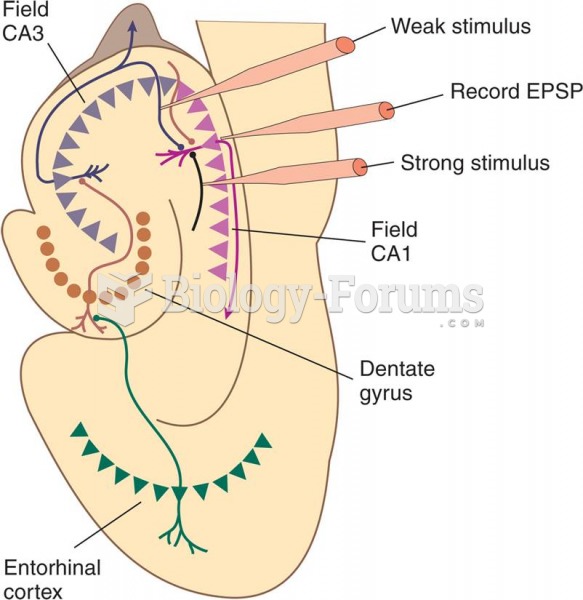
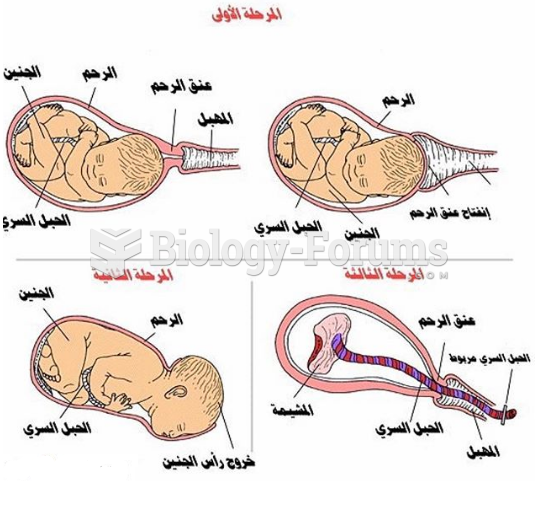
Answer to Question 1
agricultural communications
Answer to Question 2
Overall, a sustainable agricultural production system needs to be implemented that considers the environment, food production, economics, and culture. This includes:
Preserve existing land. Strategies need to be devised to protect existing land used for crop and animal production. These include conservation tillage, crop rotation, and strategic crop placement on landscapes. Irrigation strategies need to be developed to increase its efficiency and to reduce the incidence of salinization. Rural landscapes should be viewed as producers of multiple benefits: economical as well as ecological. Although increased use of land will put pressure on remaining natural ecosystems, thoughtful planning is required to balance preservation with exploitation.
Practice water conservation. There is little chance of opening up new sources of water, so sustainable water use of existing resources must be implemented. Farming practices such as increasing the amount of cover on the soil surface (using cover crops, mulches), installing high-efficiency drip irrigation, utilizing demand-based irrigation schedules, planting drought-tolerant crops, and protecting soil resources all minimize water loss and enhance infiltration of precipitation. Other land management and planting practices that minimize runoff and water loss include protecting and maintaining natural networks of water purification (wetlands, marshes) and lands that protect soil from erosion.
Develop other approaches to crop production. Although modern industrialized, high-input agriculture has worked exceptionally well in the United States, its application throughout the world has not always been successful. Alternative approaches to crop production such as organic farming that minimize inputs and fit local environmental limitations need to be expanded. In many regions of the world, the small-scale family farm may be the best way to promote a sustainable agriculture.
Increase funding for agricultural research. We should continue plant breeding and genetic engineering research that is aimed at increasing the efficiency of crop productions (e.g., increased water use or plant nutrient use efficiency) and the quality of the product while conserving genetic diversity through preservation of local indigenous plant materials. It will be important to develop crops that fit local crop production systems. In the future, we will need crops that can use marginal soils that have been compromised by salinization, acidity, or organic matter loss.
Maintain genetic diversity. We need to preserve genetic diversity of existing crops in seed banks and search for new crops that might produce food, fuel, or medicines in unique environments.
Reduce reliance on fossil fuels. We should expand the use of crops for production of renewable energy to reduce the world's growing dependence on fossil fuels. Starchy grains such as corn may provide a feedstock for a limited amount of biofuel, but their use as a human and livestock feed should be given a higher priority. Dedicated cellulosic ethanol crops such as switchgrass in the United States or sugarcane in Brazil appear to be more sustainable fuel sources.