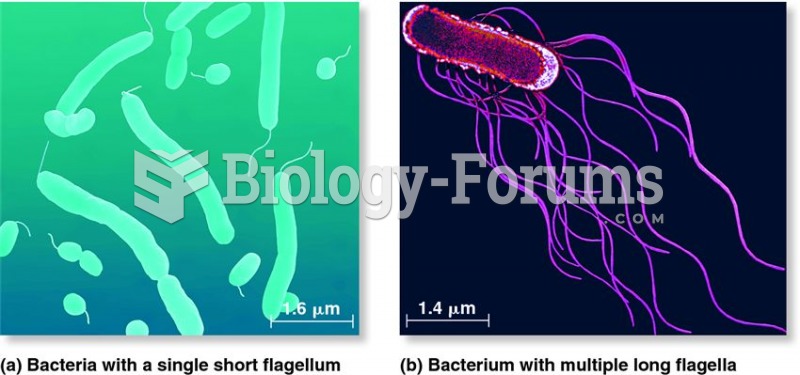
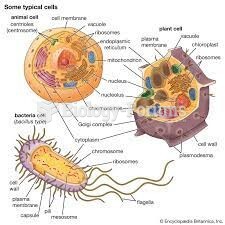
|
|
|
If you could remove all of your skin, it would weigh up to 5 pounds.
Hip fractures are the most serious consequences of osteoporosis. The incidence of hip fractures increases with each decade among patients in their 60s to patients in their 90s for both women and men of all populations. Men and women older than 80 years of age show the highest incidence of hip fractures.
Adolescents often feel clumsy during puberty because during this time of development, their hands and feet grow faster than their arms and legs do. The body is therefore out of proportion. One out of five adolescents actually experiences growing pains during this period.
In 1885, the Lloyd Manufacturing Company of Albany, New York, promoted and sold "Cocaine Toothache Drops" at 15 cents per bottle! In 1914, the Harrison Narcotic Act brought the sale and distribution of this drug under federal control.
Throughout history, plants containing cardiac steroids have been used as heart drugs and as poisons (e.g., in arrows used in combat), emetics, and diuretics.