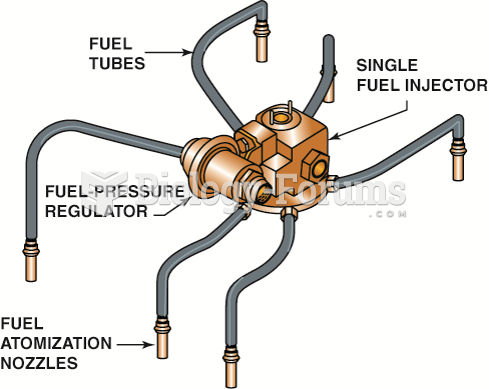
|
|
|
In 2006, a generic antinausea drug named ondansetron was approved. It is used to stop nausea and vomiting associated with surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy.
Historic treatments for rheumatoid arthritis have included gold salts, acupuncture, a diet consisting of apples or rhubarb, nutmeg, nettles, bee venom, bracelets made of copper, prayer, rest, tooth extractions, fasting, honey, vitamins, insulin, snow collected on Christmas, magnets, and electric convulsion therapy.
Acute bronchitis is an inflammation of the breathing tubes (bronchi), which causes increased mucus production and other changes. It is usually caused by bacteria or viruses, can be serious in people who have pulmonary or cardiac diseases, and can lead to pneumonia.
Fatal fungal infections may be able to resist newer antifungal drugs. Globally, fungal infections are often fatal due to the lack of access to multiple antifungals, which may be required to be utilized in combination. Single antifungals may not be enough to stop a fungal infection from causing the death of a patient.
In most cases, kidneys can recover from almost complete loss of function, such as in acute kidney (renal) failure.