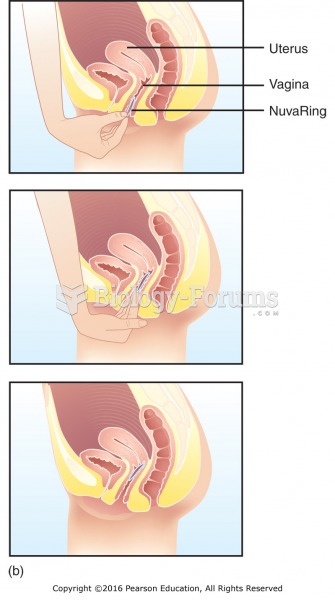
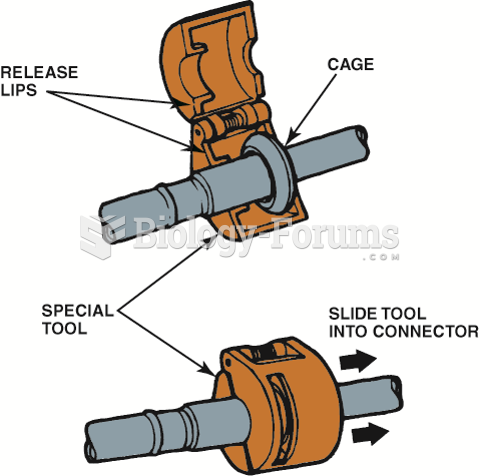
This topic contains a solution. Click here to go to the answer
|
|
|
Did you know?
The strongest synthetic topical retinoid drug available, tazarotene, is used to treat sun-damaged skin, acne, and psoriasis.
Did you know?
People about to have surgery must tell their health care providers about all supplements they take.
Did you know?
Persons who overdose with cardiac glycosides have a better chance of overall survival if they can survive the first 24 hours after the overdose.
Did you know?
Congestive heart failure is a serious disorder that carries a reduced life expectancy. Heart failure is usually a chronic illness, and it may worsen with infection or other physical stressors.
Did you know?
Increased intake of vitamin D has been shown to reduce fractures up to 25% in older people.