|
|
|
Over time, chronic hepatitis B virus and hepatitis C virus infections can progress to advanced liver disease, liver failure, and hepatocellular carcinoma. Unlike other forms, more than 80% of hepatitis C infections become chronic and lead to liver disease. When combined with hepatitis B, hepatitis C now accounts for 75% percent of all cases of liver disease around the world. Liver failure caused by hepatitis C is now leading cause of liver transplants in the United States.
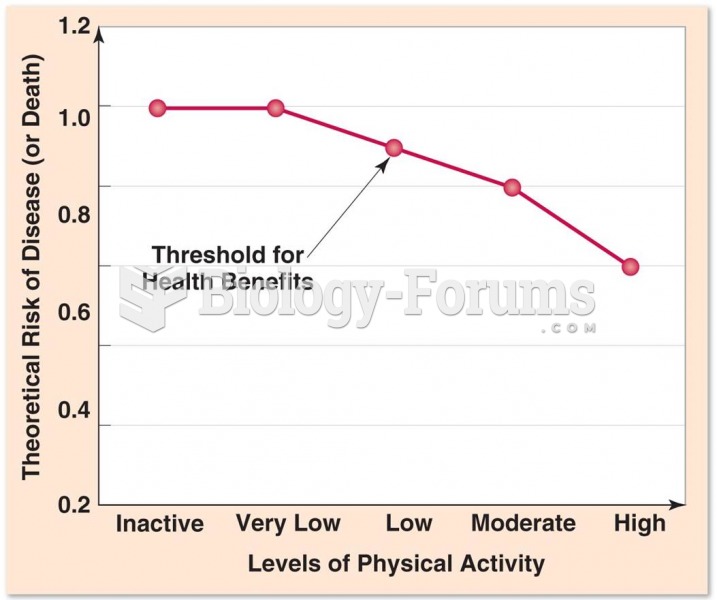
Asthma cases in Americans are about 75% higher today than they were in 1980.
In 1835 it was discovered that a disease of silkworms known as muscardine could be transferred from one silkworm to another, and was caused by a fungus.
Blastomycosis is often misdiagnosed, resulting in tragic outcomes. It is caused by a fungus living in moist soil, in wooded areas of the United States and Canada. If inhaled, the fungus can cause mild breathing problems that may worsen and cause serious illness and even death.
GI conditions that will keep you out of the U.S. armed services include ulcers, varices, fistulas, esophagitis, gastritis, congenital abnormalities, inflammatory bowel disease, enteritis, colitis, proctitis, duodenal diverticula, malabsorption syndromes, hepatitis, cirrhosis, cysts, abscesses, pancreatitis, polyps, certain hemorrhoids, splenomegaly, hernias, recent abdominal surgery, GI bypass or stomach stapling, and artificial GI openings.