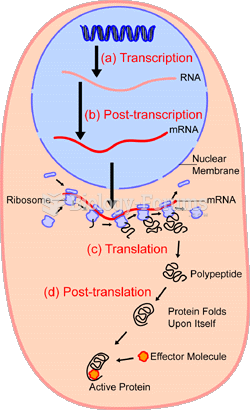
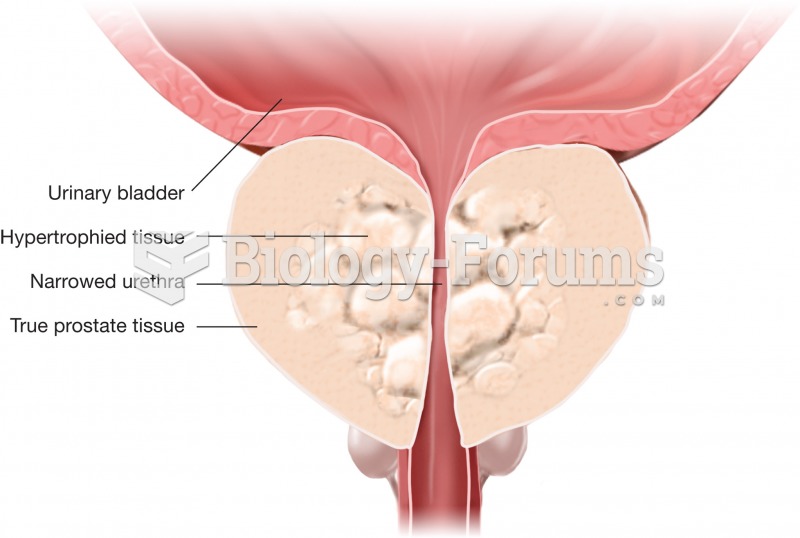
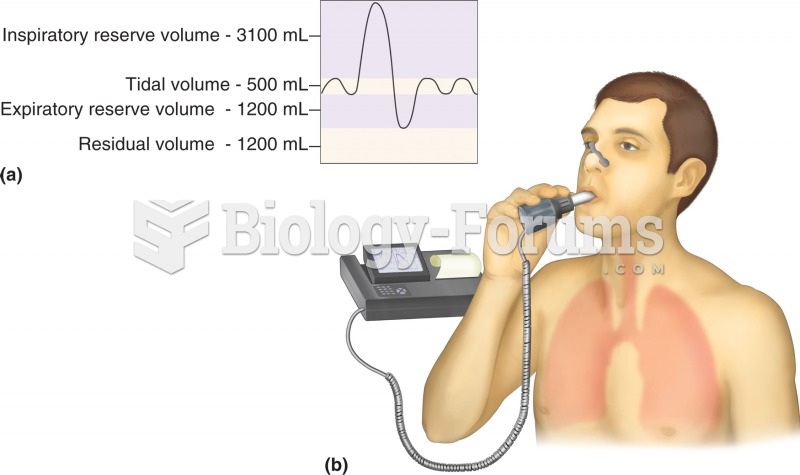
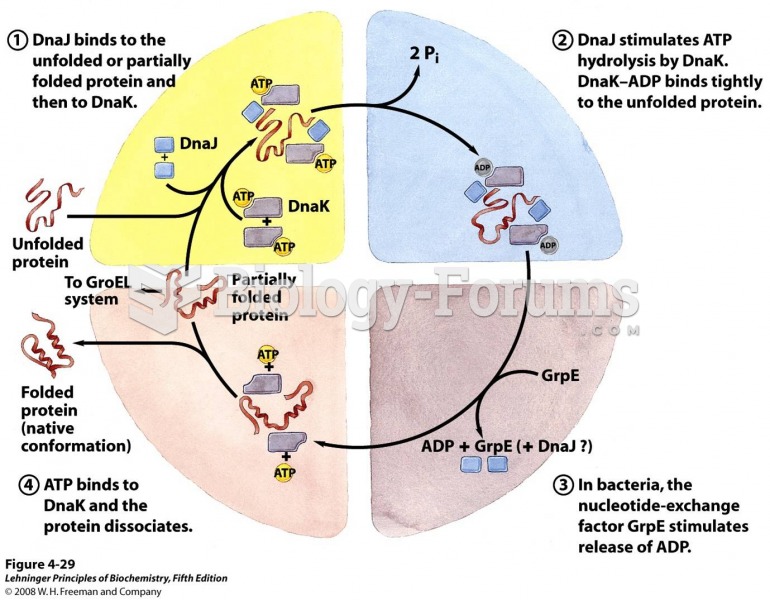
|
|
|
Patients who have undergone chemotherapy for the treatment of cancer often complain of a lack of mental focus; memory loss; and a general diminution in abilities such as multitasking, attention span, and general mental agility.
About 600,000 particles of skin are shed every hour by each human. If you live to age 70 years, you have shed 105 pounds of dead skin.
Most fungi that pathogenically affect humans live in soil. If a person is not healthy, has an open wound, or is immunocompromised, a fungal infection can be very aggressive.
All adults should have their cholesterol levels checked once every 5 years. During 2009–2010, 69.4% of Americans age 20 and older reported having their cholesterol checked within the last five years.
In most climates, 8 to 10 glasses of water per day is recommended for adults. The best indicator for adequate fluid intake is frequent, clear urination.