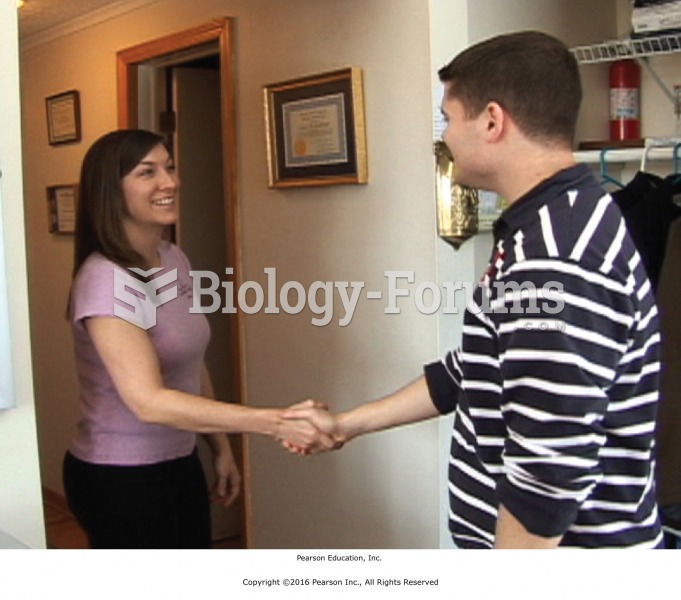
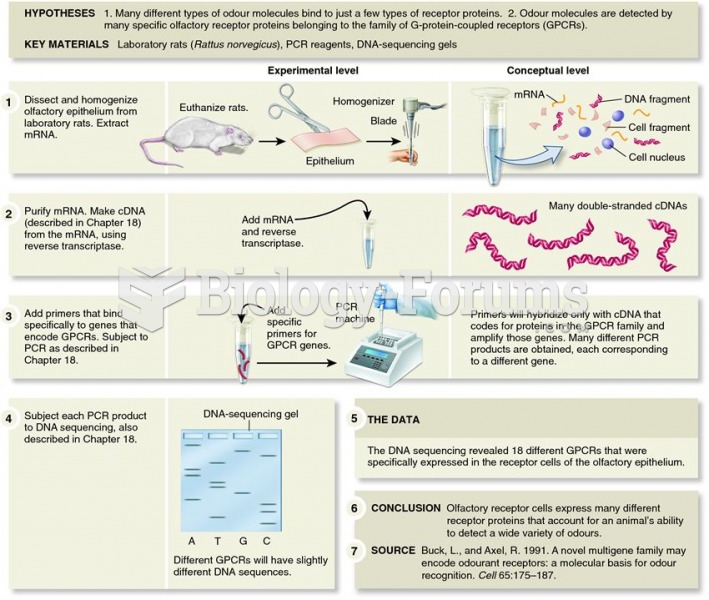
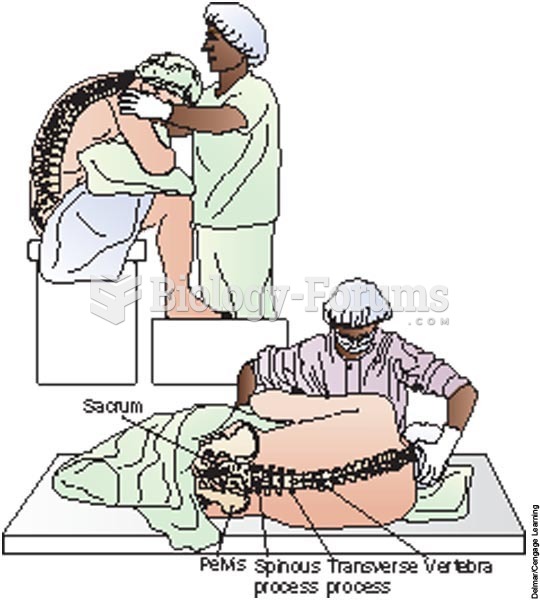
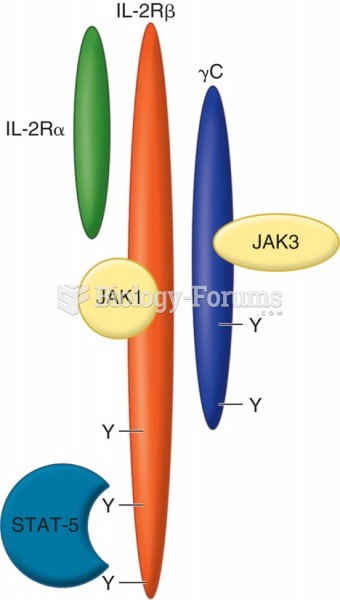
|
|
|
Complications of influenza include: bacterial pneumonia, ear and sinus infections, dehydration, and worsening of chronic conditions such as asthma, congestive heart failure, or diabetes.
According to the CDC, approximately 31.7% of the U.S. population has high low-density lipoprotein (LDL) or "bad cholesterol" levels.
The human body's pharmacokinetics are quite varied. Our hair holds onto drugs longer than our urine, blood, or saliva. For example, alcohol can be detected in the hair for up to 90 days after it was consumed. The same is true for marijuana, cocaine, ecstasy, heroin, methamphetamine, and nicotine.
Drug-induced pharmacodynamic effects manifested in older adults include drug-induced renal toxicity, which can be a major factor when these adults are experiencing other kidney problems.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has released reports detailing the deaths of infants (younger than 1 year of age) who died after being given cold and cough medications. This underscores the importance of educating parents that children younger than 2 years of age should never be given over-the-counter cold and cough medications without consulting their physicians.