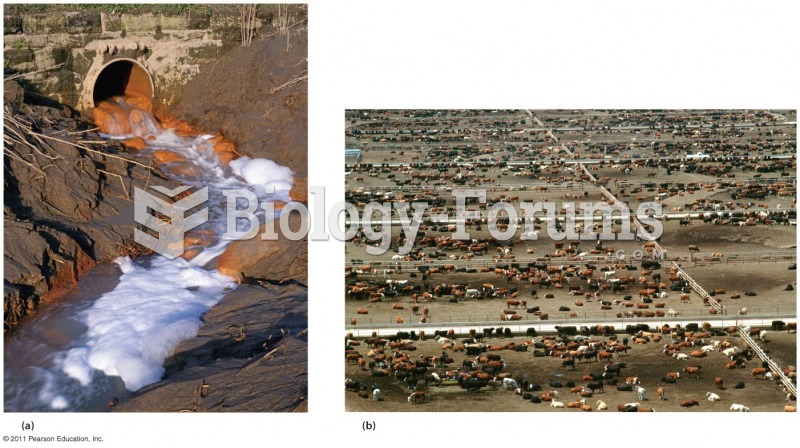
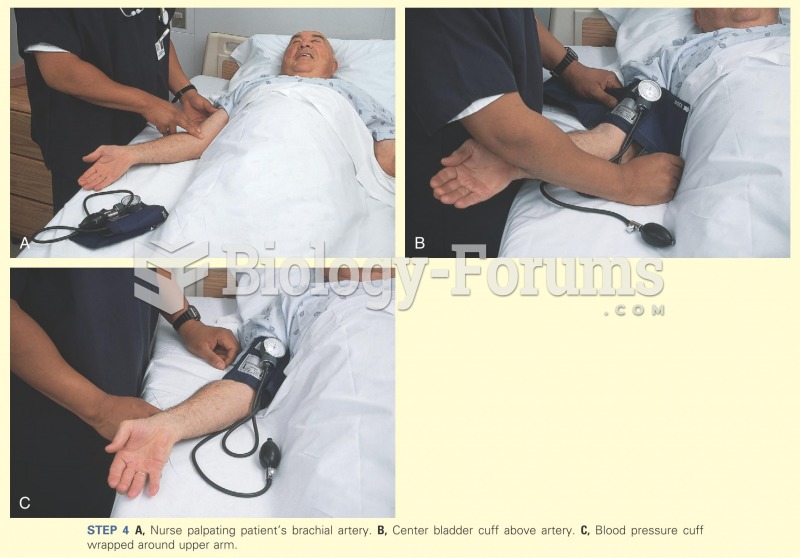
|
|
|
The first documented use of surgical anesthesia in the United States was in Connecticut in 1844.
Studies show that systolic blood pressure can be significantly lowered by taking statins. In fact, the higher the patient's baseline blood pressure, the greater the effect of statins on his or her blood pressure.
Approximately 15–25% of recognized pregnancies end in miscarriage. However, many miscarriages often occur before a woman even knows she is pregnant.
Glaucoma is a leading cause of blindness. As of yet, there is no cure. Everyone is at risk, and there may be no warning signs. It is six to eight times more common in African Americans than in whites. The best and most effective way to detect glaucoma is to receive a dilated eye examination.
The first oral chemotherapy drug for colon cancer was approved by FDA in 2001.