This topic contains a solution. Click here to go to the answer
|
|
|
Did you know?
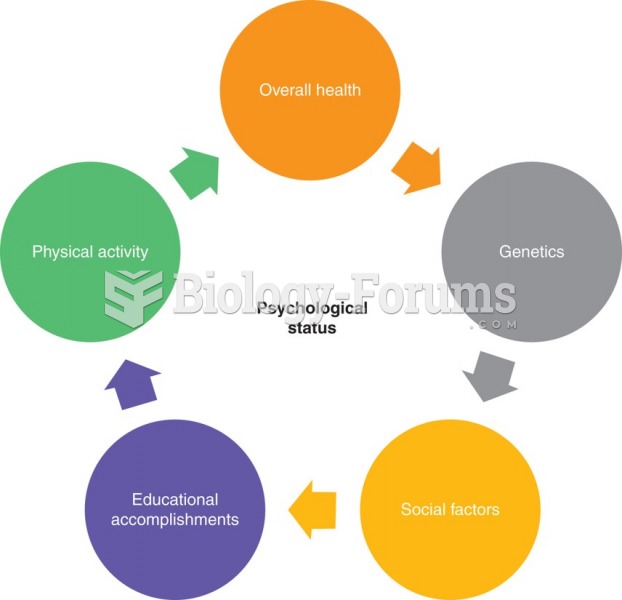
Alzheimer's disease affects only about 10% of people older than 65 years of age. Most forms of decreased mental function and dementia are caused by disuse (letting the mind get lazy).
Did you know?
Liver spots have nothing whatsoever to do with the liver. They are a type of freckles commonly seen in older adults who have been out in the sun without sufficient sunscreen.
Did you know?
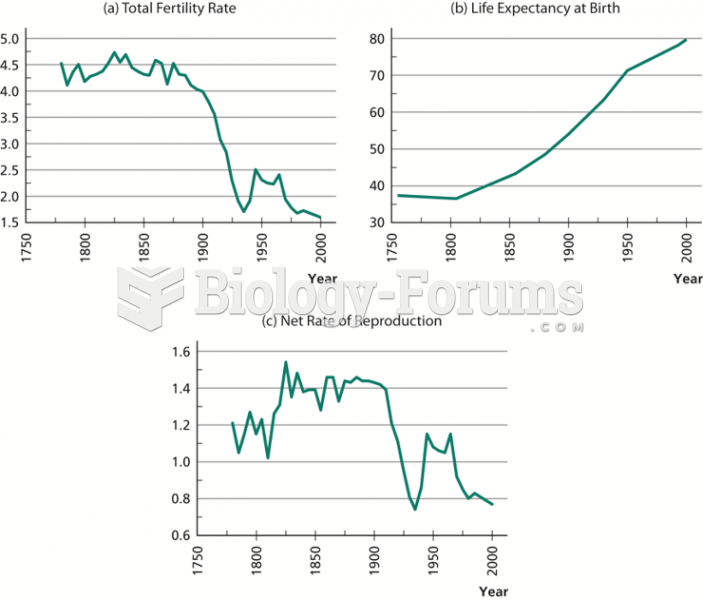
Cancer has been around as long as humankind, but only in the second half of the twentieth century did the number of cancer cases explode.
Did you know?
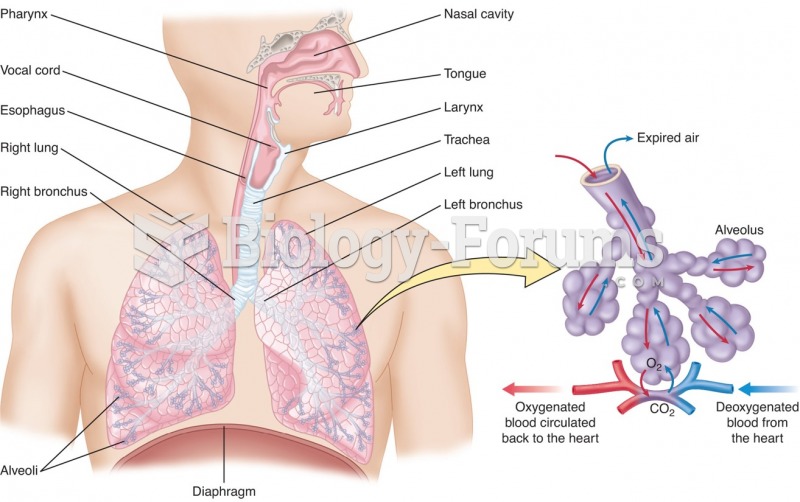
There are 60,000 miles of blood vessels in every adult human.
Did you know?
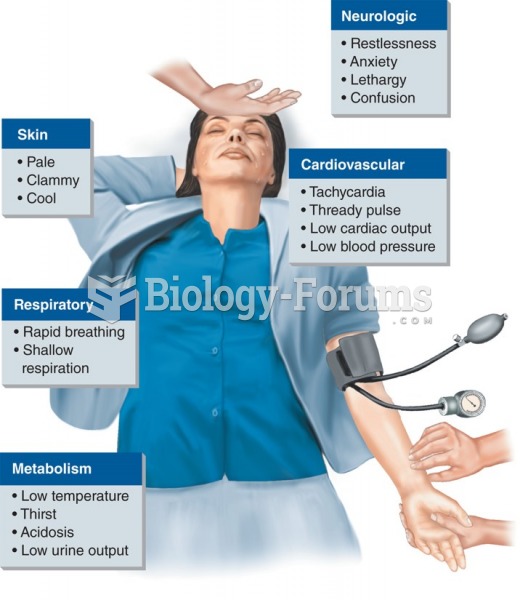
Critical care patients are twice as likely to receive the wrong medication. Of these errors, 20% are life-threatening, and 42% require additional life-sustaining treatments.