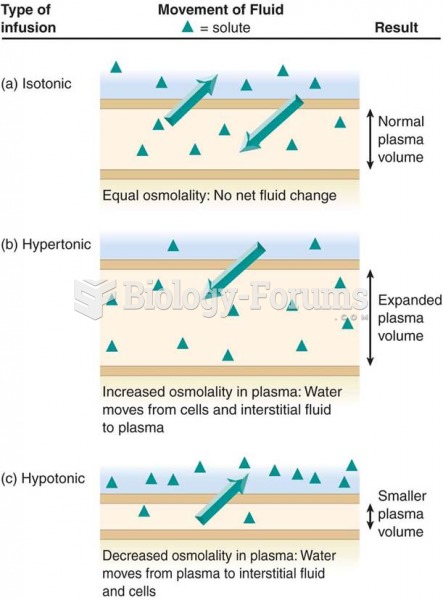
|
|
|
The word drug comes from the Dutch word droog (meaning "dry"). For centuries, most drugs came from dried plants, hence the name.
Computer programs are available that crosscheck a new drug's possible trade name with all other trade names currently available. These programs detect dangerous similarities between names and alert the manufacturer of the drug.
Pink eye is a term that refers to conjunctivitis, which is inflammation of the thin, clear membrane (conjunctiva) over the white part of the eye (sclera). It may be triggered by a virus, bacteria, or foreign body in the eye. Antibiotic eye drops alleviate bacterial conjunctivitis, and antihistamine allergy pills or eye drops help control allergic conjunctivitis symptoms.
Elderly adults are living longer, and causes of death are shifting. At the same time, autopsy rates are at or near their lowest in history.
Hippocrates noted that blood separates into four differently colored liquids when removed from the body and examined: a pure red liquid mixed with white liquid material with a yellow-colored froth at the top and a black substance that settles underneath; he named these the four humors (for blood, phlegm, yellow bile, and black bile).