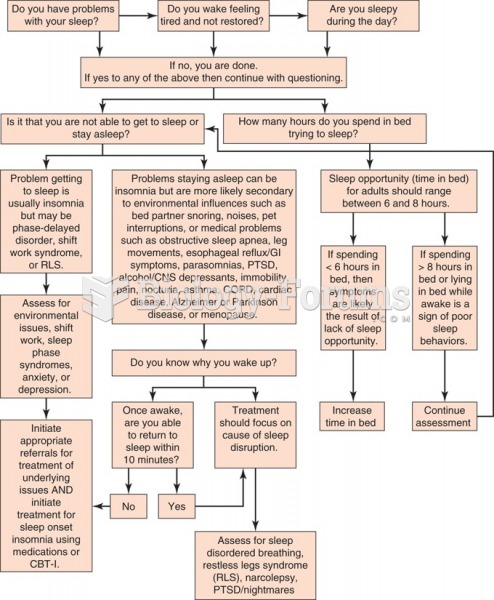
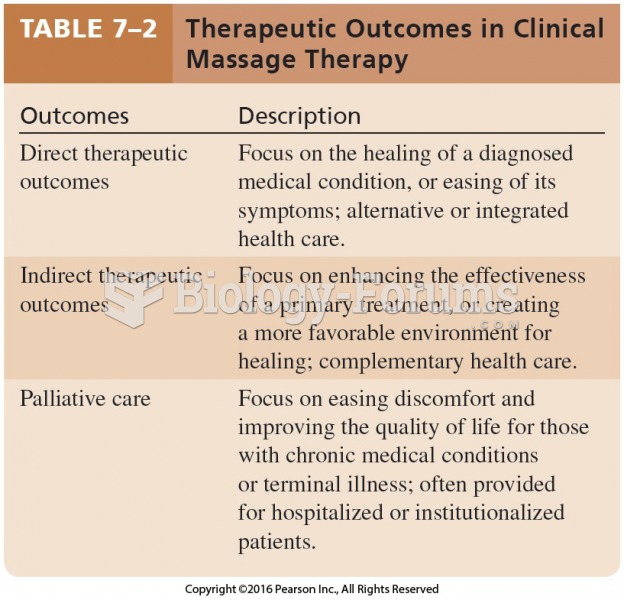
This topic contains a solution. Click here to go to the answer
|
|
|
Did you know?
Blood in the urine can be a sign of a kidney stone, glomerulonephritis, or other kidney problems.
Did you know?
Limit intake of red meat and dairy products made with whole milk. Choose skim milk, low-fat or fat-free dairy products. Limit fried food. Use healthy oils when cooking.
Did you know?
The most common treatment options for addiction include psychotherapy, support groups, and individual counseling.
Did you know?
For high blood pressure (hypertension), a new class of drug, called a vasopeptidase blocker (inhibitor), has been developed. It decreases blood pressure by simultaneously dilating the peripheral arteries and increasing the body's loss of salt.
Did you know?
Cucumber slices relieve headaches by tightening blood vessels, reducing blood flow to the area, and relieving pressure.