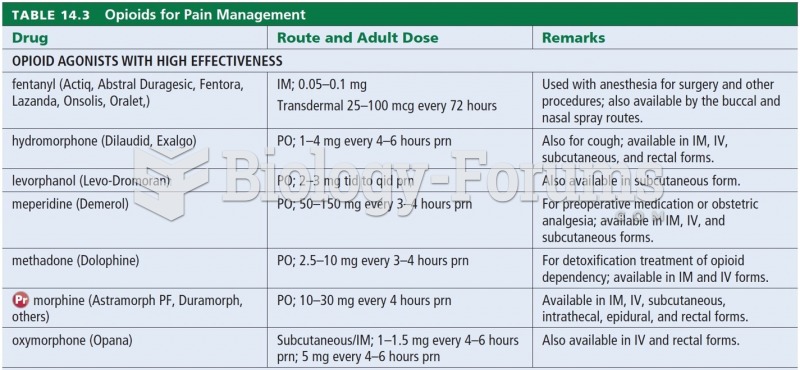
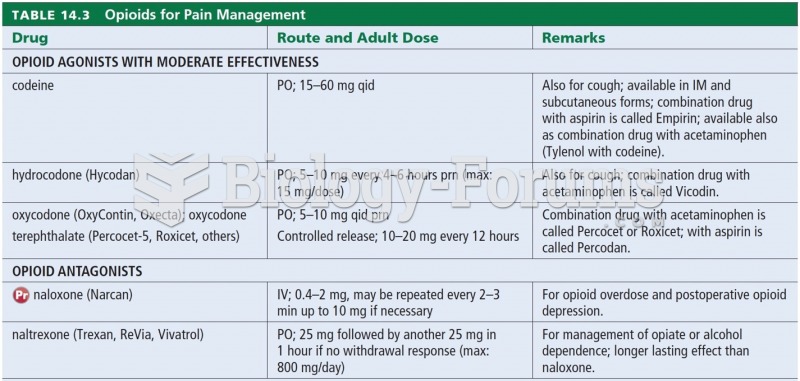
|
|
|
Sperm cells are so tiny that 400 to 500 million (400,000,000–500,000,000) of them fit onto 1 tsp.
When intravenous medications are involved in adverse drug events, their harmful effects may occur more rapidly, and be more severe than errors with oral medications. This is due to the direct administration into the bloodstream.
The average human gut is home to perhaps 500 to 1,000 different species of bacteria.
Vital signs (blood pressure, temperature, pulse rate, respiration rate) should be taken before any drug administration. Patients should be informed not to use tobacco or caffeine at least 30 minutes before their appointment.
Although puberty usually occurs in the early teenage years, the world's youngest parents were two Chinese children who had their first baby when they were 8 and 9 years of age.