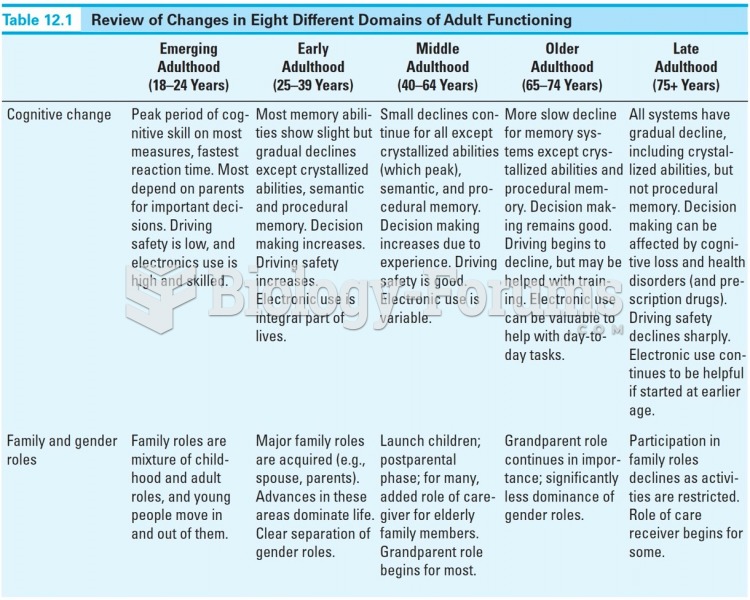
Answer to Question 1
Correct Answer: 1,2,3
Rationale 1: Liver function declines during the aging process.
Rationale 2: As liver function declines, so does the production of plasma proteins.
Rationale 3: As the production of plasma proteins declines, an increase in highly protein-bound drugs results in higher concentrations of free drug.
Rationale 4: Decreased plasma proteins lead to fewer binding sites, resulting in higher, not lower, concentrations of free drug.
Rationale 5: The decrease in liver function and plasma proteins may cause the adverse effects of bleeding and bloody stools. It does not have anything to do with the bloodbrain barrier.
Global Rationale: Liver function declines during the aging process. As liver function declines, so does the production of plasma proteins. As the production of plasma proteins declines, an increase in highly protein-bound drugs results in higher concentrations of free drug. Decreased plasma proteins lead to fewer binding sites, resulting in higher, not lower, concentrations of free drug. The decrease in liver function and plasma proteins may cause the adverse effects of bleeding and bloody stools. It does not have anything to do with the bloodbrain barrier.
Answer to Question 2
Correct Answer: 1,2,3
Rationale 1: Age-related changes result in a decrease in total body water in the older adult. Because gentamicin is water soluble, this could result in higher concentration of the drug, causing toxicity.
Rationale 2: To prevent toxicity of gentamicin, periodic lab work for peak and trough must be checked.
Rationale 3: If the serum concentration is not within therapeutic range, the dose may need to be adjusted.
Rationale 4: Drugs with a long half-life have the potential to accumulate in the tissues. These drugs should be prescribed with longer intervals between doses.
Rationale 5: Gentamicin toxicity symptoms include impaired hearing, not reduced cognitive function or confusion.
Global Rationale: Age-related changes result in a decrease in total body water in the older adult. Because gentamicin is water soluble, this could result in higher concentration of the drug, causing toxicity. To prevent toxicity of gentamicin, periodic lab work for peak and trough must be checked. If the serum concentration is not within therapeutic range, the dose may need to be adjusted. Drugs with a long half-life have the potential to accumulate in the tissues. These drugs should be prescribed with longer intervals between doses. Gentamicin toxicity symptoms include impaired hearing, not reduced cognitive function or confusion.