Answer to Question 1
Correct Answer: 1,2,3
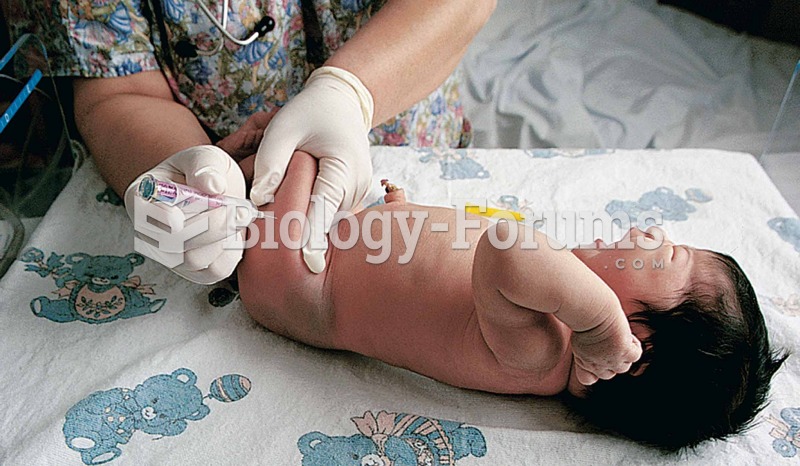
Rationale 1: The vastus lateralis muscle is the preferred site for IM injections in toddlers because there are few nerves and the muscle is well developed.
Rationale 2: After the child has been walking for a year, the ventrogluteal site is used for IM injections because it causes less pain than the vastus lateralis.
Rationale 3: Use of the dorsogluteal site has declined due to the risk of affecting the sciatic nerve.
Rationale 4: The vastus lateralis muscle is the preferred site for IM injections in toddlers, not preschoolers.
Rationale 5: Use of the dorsogluteal site has declined due to the risk of affecting the sciatic nerve.
Global Rationale: The vastus lateralis muscle is the preferred site for IM injections in toddlers (not preschoolers) because there are few nerves and the muscle is well developed. After the child has been walking for a year, the ventrogluteal site is used for IM injections because it causes less pain than the vastus lateralis. Use of the dorsogluteal site has declined due to the risk of affecting the sciatic nerve.
Answer to Question 2
Correct Answer: 1,2,3
Rationale 1: High expectations of a successful outcome will help clients adhere to a medication regimen. If the medication does not meet these expectations, the client may stop taking it.
Rationale 2: Clients are more likely to follow a medication regimen if they have supportive family members.
Rationale 3: Clients are more likely to adhere to a medication regimen if there are minimal adverse effects. Teaching the client to take this medication with food may decrease the nausea and improve adherence.
Rationale 4: Positive interactions with staff may increase adherence.
Rationale 5: A simple, short-term, inexpensive regimen with minimum daily disruption helps to increase adherence.
Global Rationale: High expectations of a successful outcome will help clients adhere to a medication regimen. If the medication does not meet these expectations, the client may stop taking it. Clients are more likely to follow a medication regimen if they have supportive family members. Clients are more likely to adhere to a medication regimen if there are minimal adverse effects. Teaching the client to take this medication with food may decrease the nausea and improve adherence. Positive interactions with staff may increase adherence. A simple, short-term, inexpensive regimen with minimum daily disruption helps to increase adherence.