|
|
|
It is important to read food labels and choose foods with low cholesterol and saturated trans fat. You should limit saturated fat to no higher than 6% of daily calories.
In Eastern Europe and Russia, interferon is administered intranasally in varied doses for the common cold and influenza. It is claimed that this treatment can lower the risk of infection by as much as 60–70%.
People with high total cholesterol have about two times the risk for heart disease as people with ideal levels.
A cataract is a clouding of the eyes' natural lens. As we age, some clouding of the lens may occur. The first sign of a cataract is usually blurry vision. Although glasses and other visual aids may at first help a person with cataracts, surgery may become inevitable. Cataract surgery is very successful in restoring vision, and it is the most frequently performed surgery in the United States.
The liver is the only organ that has the ability to regenerate itself after certain types of damage. As much as 25% of the liver can be removed, and it will still regenerate back to its original shape and size. However, the liver cannot regenerate after severe damage caused by alcohol.
 In many industrialized nations, men are having children at older ages, raising the possibility of ...
In many industrialized nations, men are having children at older ages, raising the possibility of ...
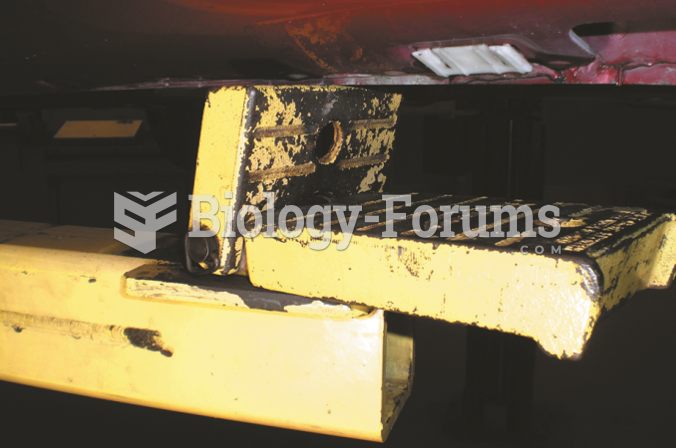 If raising a vehicle without a frame, place the flat pads under the pinch weld seam to spread the ...
If raising a vehicle without a frame, place the flat pads under the pinch weld seam to spread the ...