This topic contains a solution. Click here to go to the answer
|
|
|
Did you know?
The first oral chemotherapy drug for colon cancer was approved by FDA in 2001.
Did you know?
More than 4.4billion prescriptions were dispensed within the United States in 2016.
Did you know?
A strange skin disease referred to as Morgellons has occurred in the southern United States and in California. Symptoms include slowly healing sores, joint pain, persistent fatigue, and a sensation of things crawling through the skin. Another symptom is strange-looking, threadlike extrusions coming out of the skin.
Did you know?
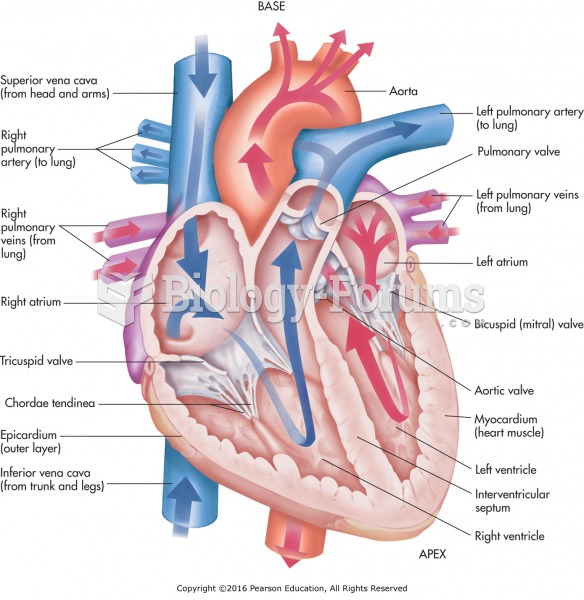
There are 60,000 miles of blood vessels in every adult human.
Did you know?
Amphetamine poisoning can cause intravascular coagulation, circulatory collapse, rhabdomyolysis, ischemic colitis, acute psychosis, hyperthermia, respiratory distress syndrome, and pericarditis.