|
|
|
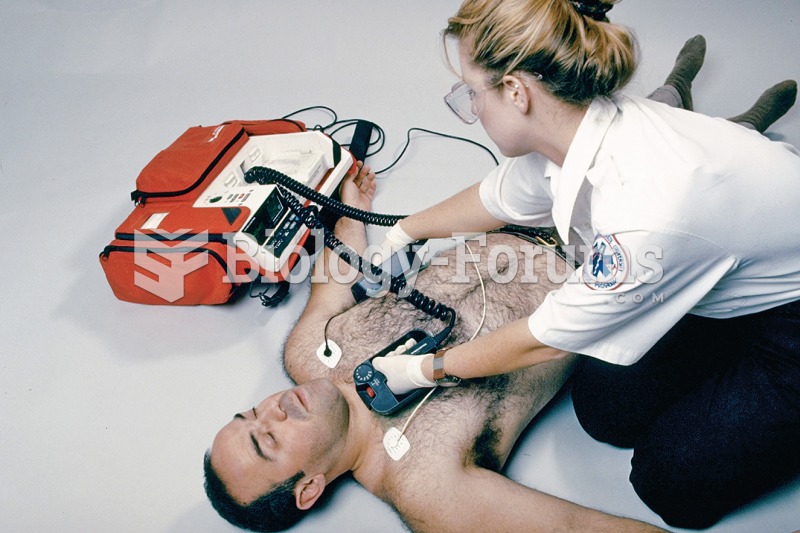
Signs and symptoms of a drug overdose include losing consciousness, fever or sweating, breathing problems, abnormal pulse, and changes in skin color.
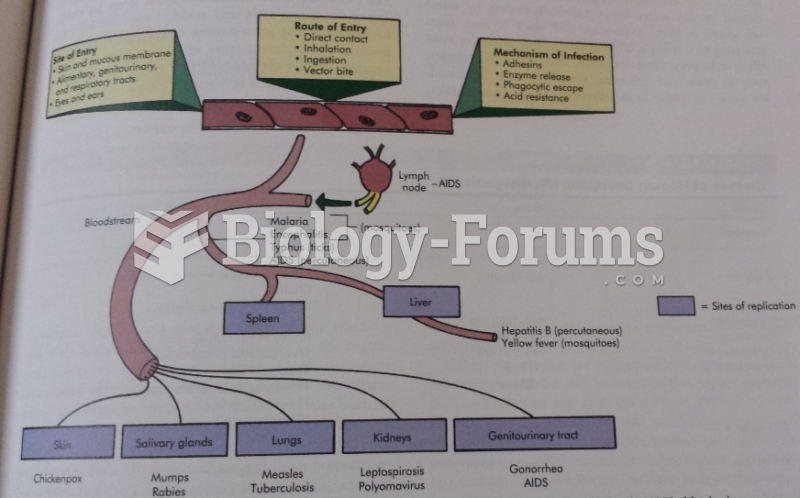
Acute bronchitis is an inflammation of the breathing tubes (bronchi), which causes increased mucus production and other changes. It is usually caused by bacteria or viruses, can be serious in people who have pulmonary or cardiac diseases, and can lead to pneumonia.
Signs and symptoms that may signify an eye tumor include general blurred vision, bulging eye(s), double vision, a sensation of a foreign body in the eye(s), iris defects, limited ability to move the eyelid(s), limited ability to move the eye(s), pain or discomfort in or around the eyes or eyelids, red or pink eyes, white or cloud spots on the eye(s), colored spots on the eyelid(s), swelling around the eyes, swollen eyelid(s), and general vision loss.
Today, nearly 8 out of 10 pregnant women living with HIV (about 1.1 million), receive antiretrovirals.
A headache when you wake up in the morning is indicative of sinusitis. Other symptoms of sinusitis can include fever, weakness, tiredness, a cough that may be more severe at night, and a runny nose or nasal congestion.