|
|
|
The immune system needs 9.5 hours of sleep in total darkness to recharge completely.
The ratio of hydrogen atoms to oxygen in water (H2O) is 2:1.
Elderly adults are at greatest risk of stroke and myocardial infarction and have the most to gain from prophylaxis. Patients ages 60 to 80 years with blood pressures above 160/90 mm Hg should benefit from antihypertensive treatment.
When blood is deoxygenated and flowing back to the heart through the veins, it is dark reddish-blue in color. Blood in the arteries that is oxygenated and flowing out to the body is bright red. Whereas arterial blood comes out in spurts, venous blood flows.
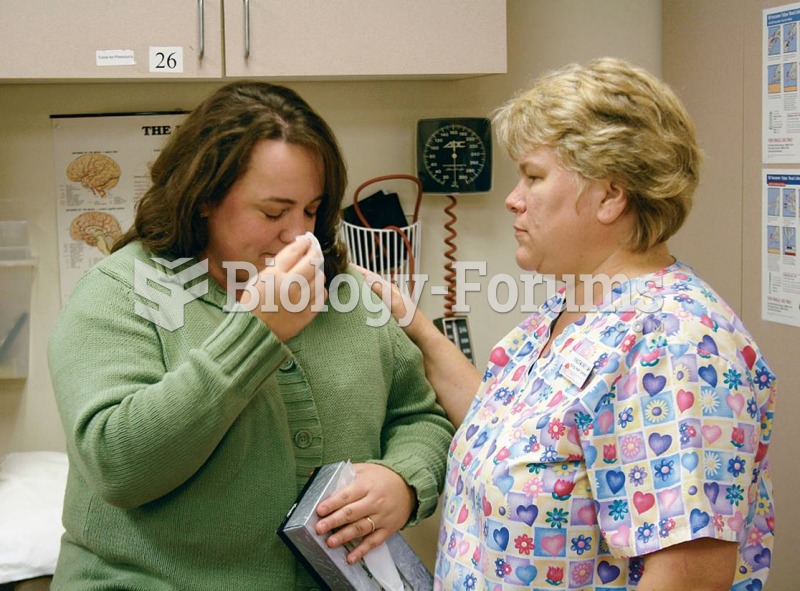
Every flu season is different, and even healthy people can get extremely sick from the flu, as well as spread it to others. The flu season can begin as early as October and last as late as May. Every person over six months of age should get an annual flu vaccine. The vaccine cannot cause you to get influenza, but in some seasons, may not be completely able to prevent you from acquiring influenza due to changes in causative viruses. The viruses in the flu shot are killed—there is no way they can give you the flu. Minor side effects include soreness, redness, or swelling where the shot was given. It is possible to develop a slight fever, and body aches, but these are simply signs that the body is responding to the vaccine and making itself ready to fight off the influenza virus should you come in contact with it.
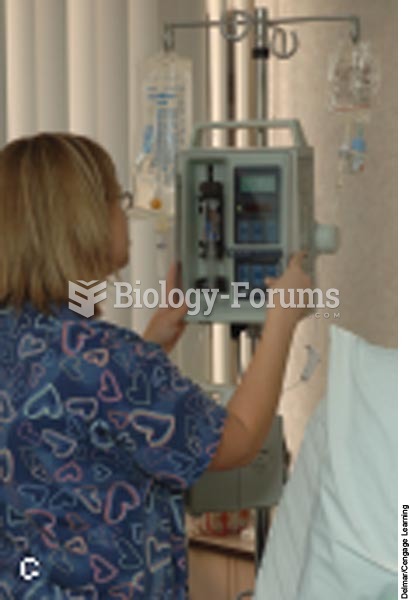 C, A nurse can also administer the medication by setting the dose and rate with an electronic infusi
C, A nurse can also administer the medication by setting the dose and rate with an electronic infusi
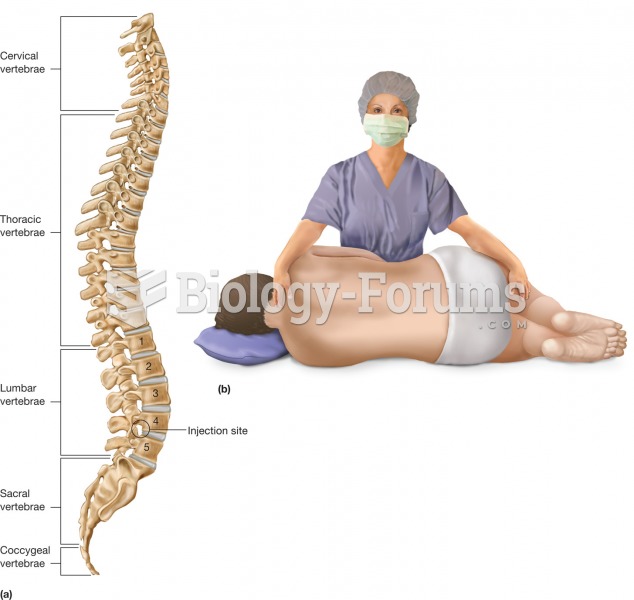 Lumbar puncture. Abbreviated LP, the lumbar puncture is a common procedure that withdraws cerebrospi
Lumbar puncture. Abbreviated LP, the lumbar puncture is a common procedure that withdraws cerebrospi
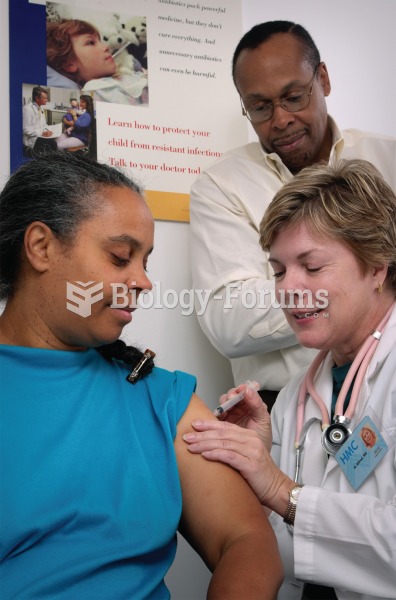 Immunization with a vaccine. A healthcare professional is injecting a vaccine into the patient’s arm
Immunization with a vaccine. A healthcare professional is injecting a vaccine into the patient’s arm




