This topic contains a solution. Click here to go to the answer
|
|
|
Did you know?
Pubic lice (crabs) are usually spread through sexual contact. You cannot catch them by using a public toilet.
Did you know?
Illicit drug use costs the United States approximately $181 billion every year.
Did you know?
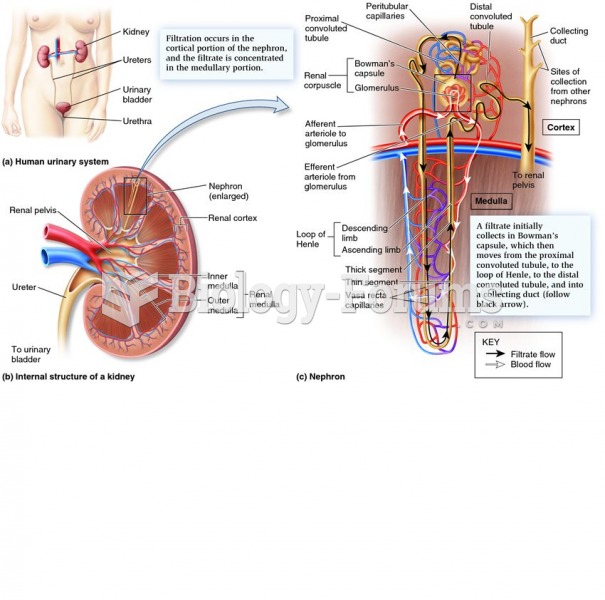
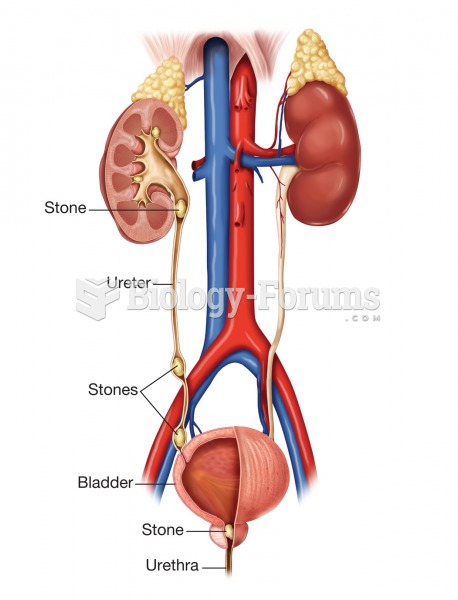
Blood in the urine can be a sign of a kidney stone, glomerulonephritis, or other kidney problems.
Did you know?
The newest statin drug, rosuvastatin, has been called a superstatin because it appears to reduce LDL cholesterol to a greater degree than the other approved statin drugs.
Did you know?
Recent studies have shown that the number of medication errors increases in relation to the number of orders that are verified per pharmacist, per work shift.