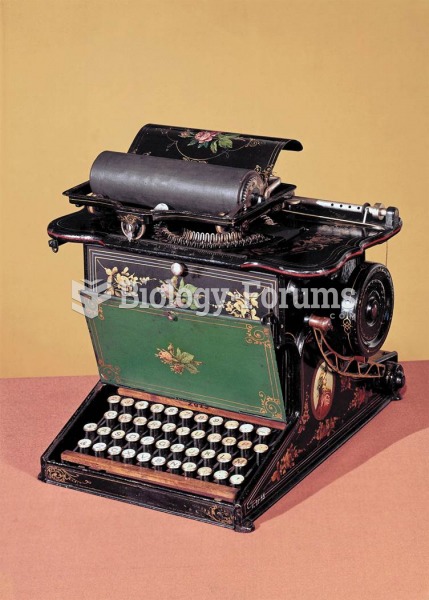
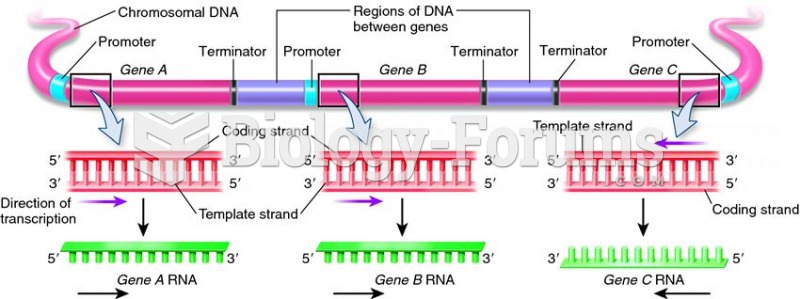
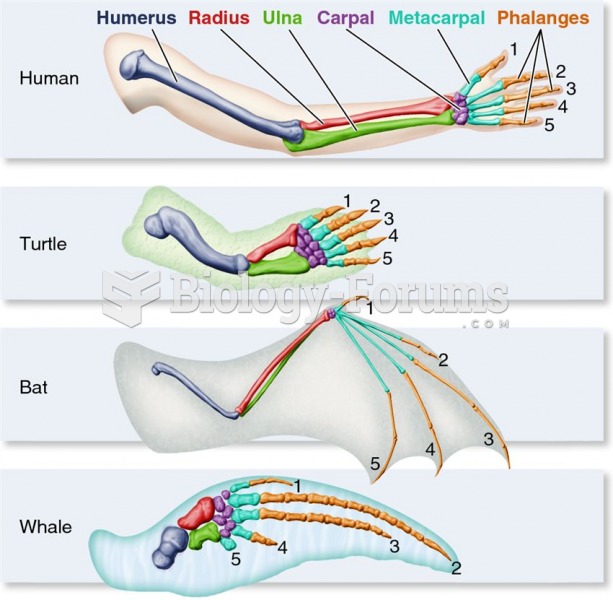
|
|
|
Certain rare plants containing cyanide include apricot pits and a type of potato called cassava. Fortunately, only chronic or massive ingestion of any of these plants can lead to serious poisoning.
About 3% of all pregnant women will give birth to twins, which is an increase in rate of nearly 60% since the early 1980s.
In the United States, there is a birth every 8 seconds, according to the U.S. Census Bureau's Population Clock.
As many as 28% of hospitalized patients requiring mechanical ventilators to help them breathe (for more than 48 hours) will develop ventilator-associated pneumonia. Current therapy involves intravenous antibiotics, but new antibiotics that can be inhaled (and more directly treat the infection) are being developed.
The eye muscles are the most active muscles in the whole body. The external muscles that move the eyes are the strongest muscles in the human body for the job they have to do. They are 100 times more powerful than they need to be.
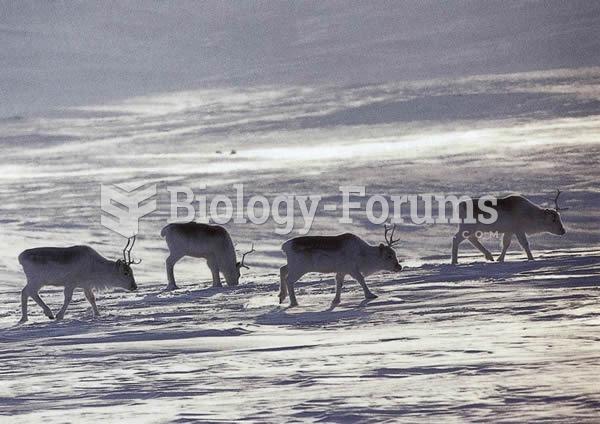 The Peary caribou is a relatively small and pale subspecies found in the tundra of far northern Nort
The Peary caribou is a relatively small and pale subspecies found in the tundra of far northern Nort
 The yellow-winged darter, Sympetrum flaveolum, is a dragonfly found in Europe and mid and Northern C
The yellow-winged darter, Sympetrum flaveolum, is a dragonfly found in Europe and mid and Northern C