- Grade 11 and 12 Mathematics (Moderator: geoffrey)
|
|
|
- Grade 11 and 12 Mathematics (Moderator: geoffrey)
The average person is easily confused by the terms pharmaceutics and pharmacology, thinking they are one and the same. Whereas pharmaceutics is the science of preparing and dispensing drugs (otherwise known as the science of pharmacy), pharmacology is the study of medications.
Sildenafil (Viagra®) has two actions that may be of consequence in patients with heart disease. It can lower the blood pressure, and it can interact with nitrates. It should never be used in patients who are taking nitrates.
Increased intake of vitamin D has been shown to reduce fractures up to 25% in older people.
Barbituric acid, the base material of barbiturates, was first synthesized in 1863 by Adolph von Bayer. His company later went on to synthesize aspirin for the first time, and Bayer aspirin is still a popular brand today.
The shortest mature adult human of whom there is independent evidence was Gul Mohammed in India. In 1990, he was measured in New Delhi and stood 22.5 inches tall.
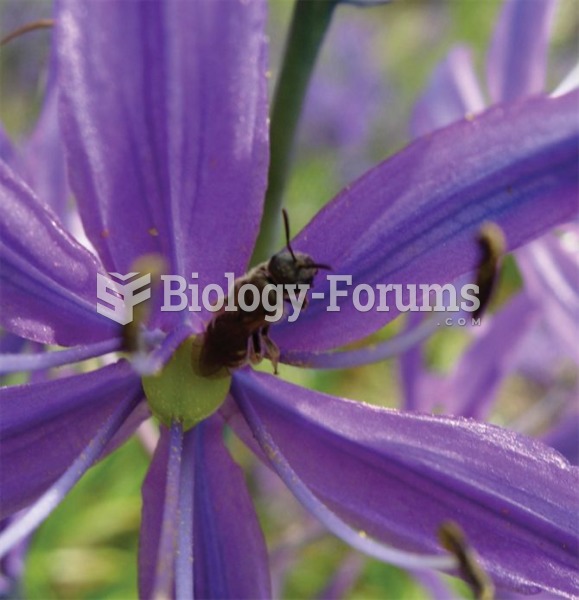 Mutualisms, such as those that occur among plants and pollinators, generally involve large numbers o
Mutualisms, such as those that occur among plants and pollinators, generally involve large numbers o
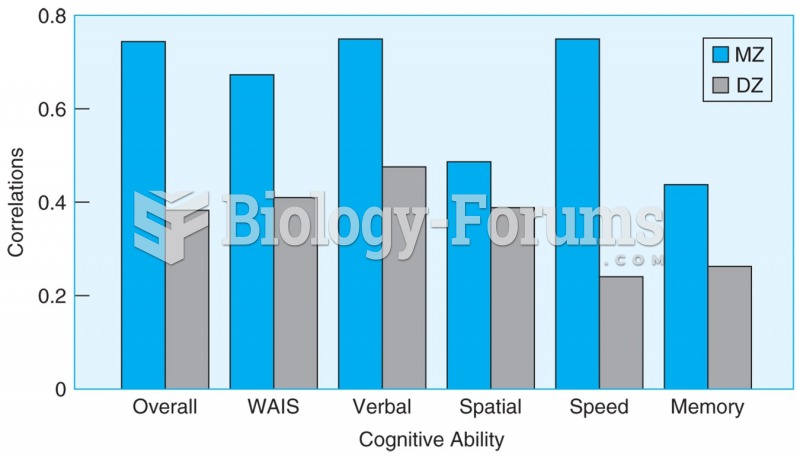 Correlations on tests for a number of cognitive abilities are higher for monozygotic twin pairs (who ...
Correlations on tests for a number of cognitive abilities are higher for monozygotic twin pairs (who ...