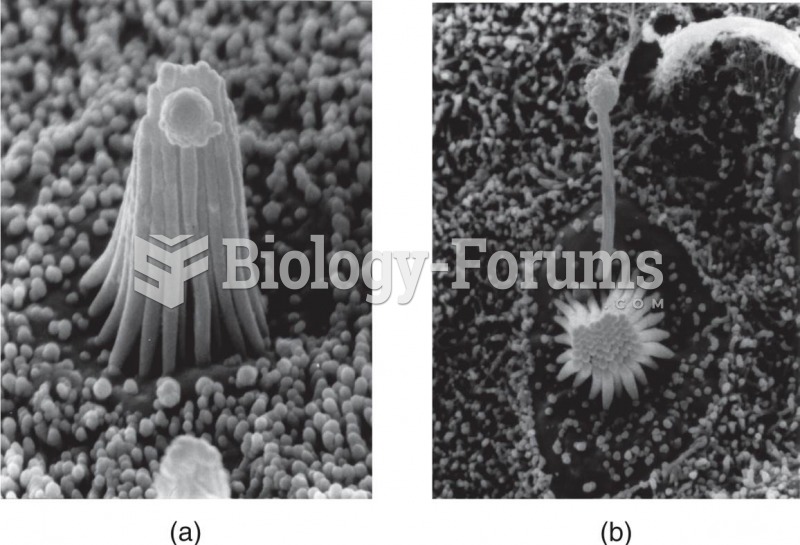
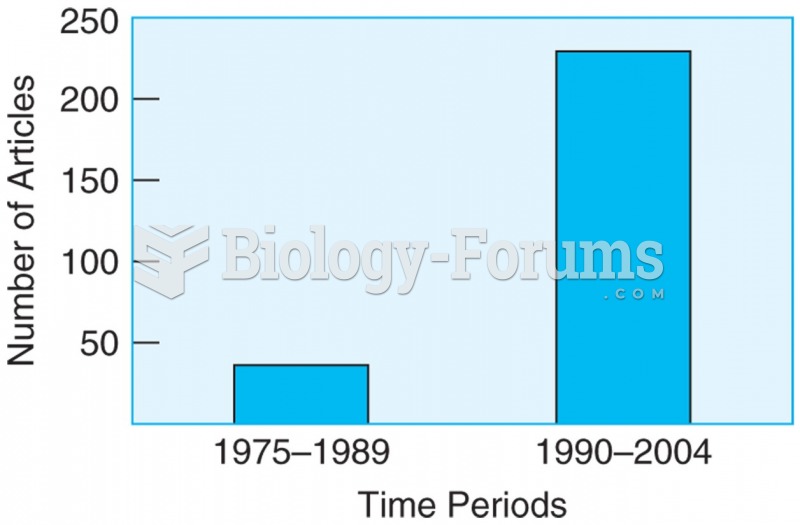
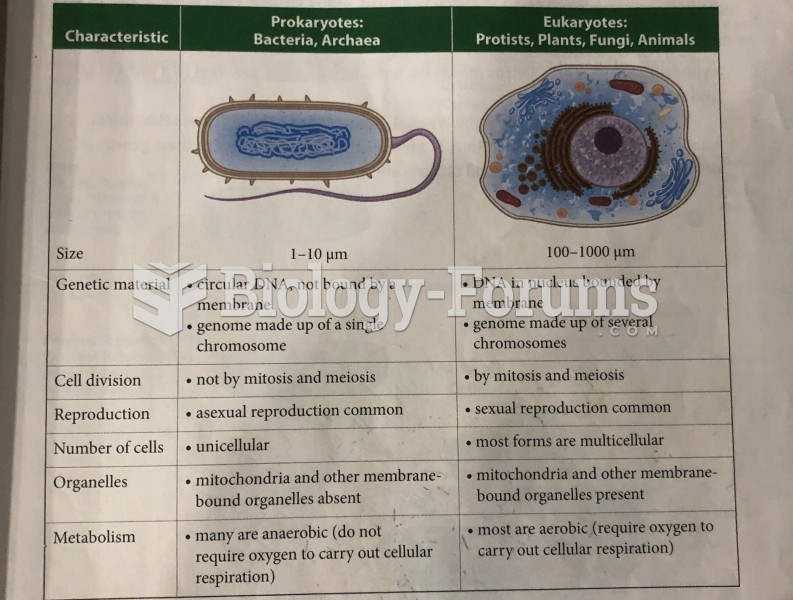
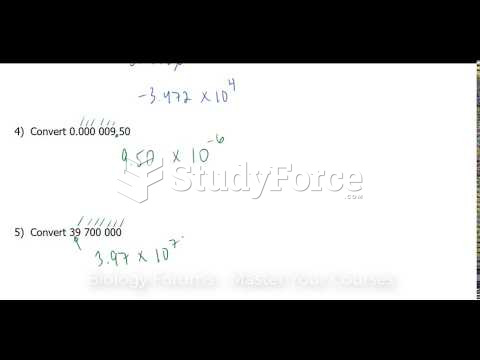- Grade 11 and 12 Mathematics (Moderator: geoffrey)
This topic contains a solution. Click here to go to the answer
|
|
|
- Grade 11 and 12 Mathematics (Moderator: geoffrey)
Did you know?
There are more nerve cells in one human brain than there are stars in the Milky Way.
Did you know?
On average, the stomach produces 2 L of hydrochloric acid per day.
Did you know?
Amphetamine poisoning can cause intravascular coagulation, circulatory collapse, rhabdomyolysis, ischemic colitis, acute psychosis, hyperthermia, respiratory distress syndrome, and pericarditis.
Did you know?
Human kidneys will clean about 1 million gallons of blood in an average lifetime.
Did you know?
During the twentieth century, a variant of the metric system was used in Russia and France in which the base unit of mass was the tonne. Instead of kilograms, this system used millitonnes (mt).