- Grade 11 and 12 Mathematics (Moderator: geoffrey)
|
|
|
- Grade 11 and 12 Mathematics (Moderator: geoffrey)
A good example of polar molecules can be understood when trying to make a cake. If water and oil are required, they will not mix together. If you put them into a measuring cup, the oil will rise to the top while the water remains on the bottom.
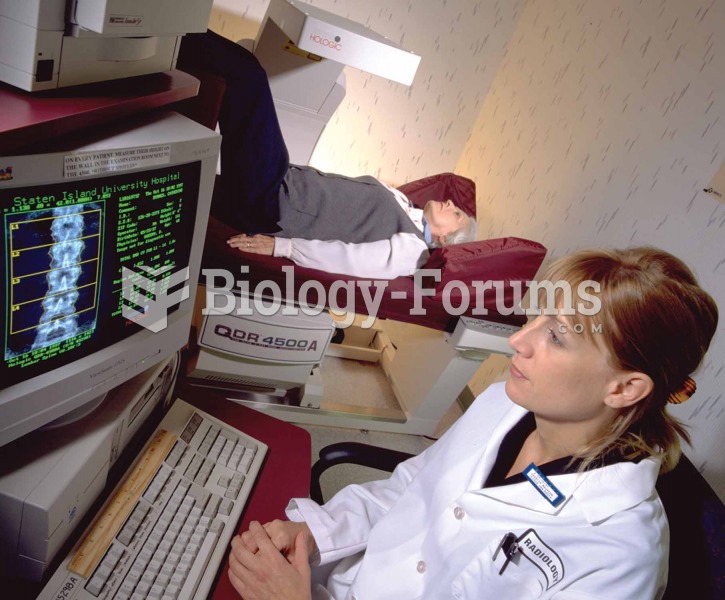
HIV testing reach is still limited. An estimated 40% of people with HIV (more than 14 million) remain undiagnosed and do not know their infection status.
Addicts to opiates often avoid treatment because they are afraid of withdrawal. Though unpleasant, with proper management, withdrawal is rarely fatal and passes relatively quickly.
On average, the stomach produces 2 L of hydrochloric acid per day.
Not getting enough sleep can greatly weaken the immune system. Lack of sleep makes you more likely to catch a cold, or more difficult to fight off an infection.