- Grade 11 and 12 Mathematics (Moderator: geoffrey)
|
|
|
- Grade 11 and 12 Mathematics (Moderator: geoffrey)
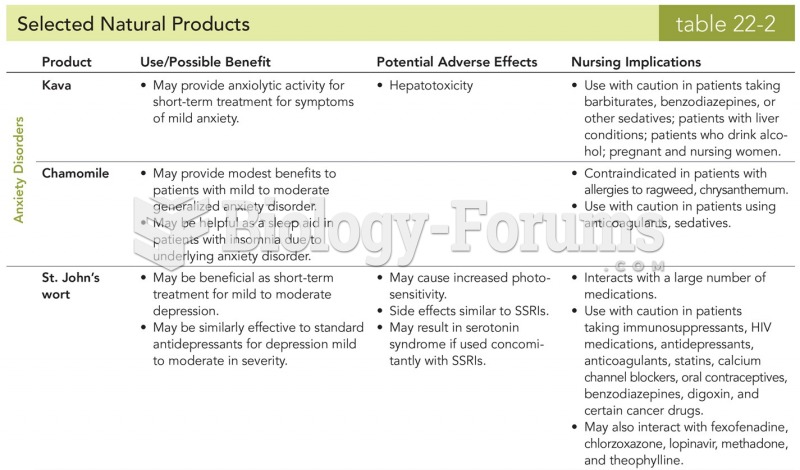
The word drug comes from the Dutch word droog (meaning "dry"). For centuries, most drugs came from dried plants, hence the name.
There are major differences in the metabolism of morphine and the illegal drug heroin. Morphine mostly produces its CNS effects through m-receptors, and at k- and d-receptors. Heroin has a slight affinity for opiate receptors. Most of its actions are due to metabolism to active metabolites (6-acetylmorphine, morphine, and morphine-6-glucuronide).
Of the estimated 2 million heroin users in the United States, 600,000–800,000 are considered hardcore addicts. Heroin addiction is considered to be one of the hardest addictions to recover from.
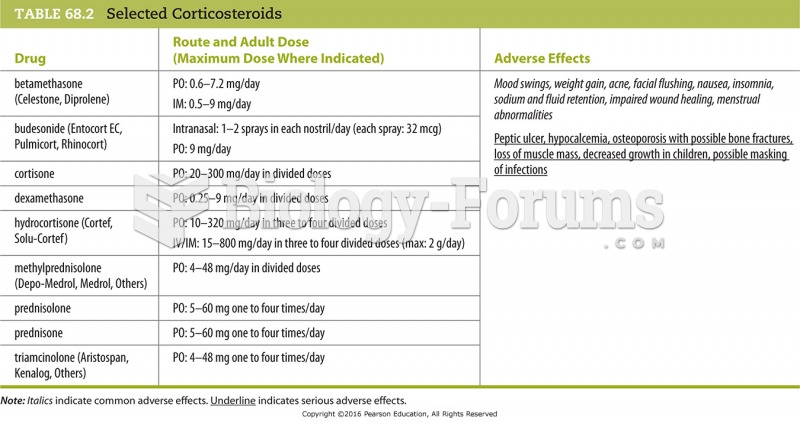
Bacteria have been found alive in a lake buried one half mile under ice in Antarctica.
GI conditions that will keep you out of the U.S. armed services include ulcers, varices, fistulas, esophagitis, gastritis, congenital abnormalities, inflammatory bowel disease, enteritis, colitis, proctitis, duodenal diverticula, malabsorption syndromes, hepatitis, cirrhosis, cysts, abscesses, pancreatitis, polyps, certain hemorrhoids, splenomegaly, hernias, recent abdominal surgery, GI bypass or stomach stapling, and artificial GI openings.