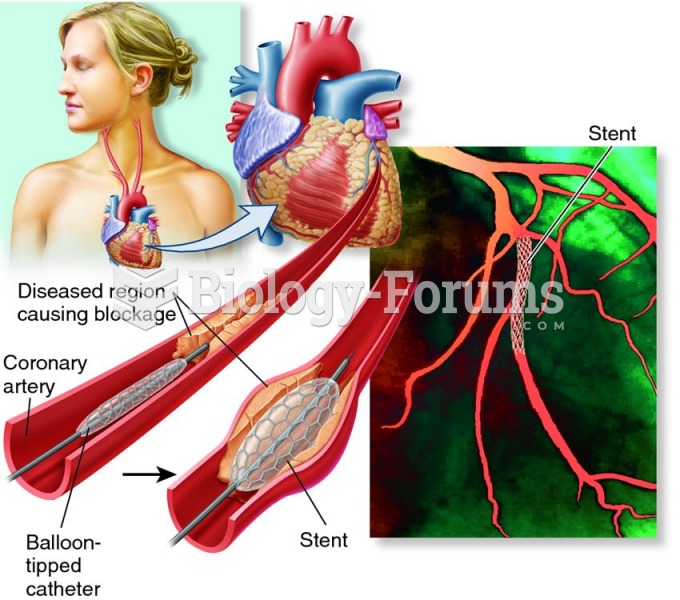
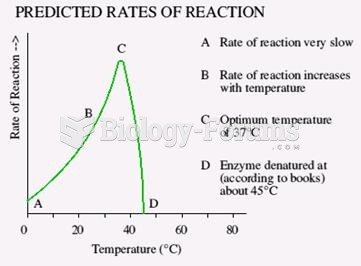
This topic contains a solution. Click here to go to the answer
|
|
|
Did you know?
Nitroglycerin is used to alleviate various heart-related conditions, and it is also the chief component of dynamite (but mixed in a solid clay base to stabilize it).
Did you know?
Famous people who died from poisoning or drug overdose include, Adolf Hitler, Socrates, Juan Ponce de Leon, Marilyn Monroe, Judy Garland, and John Belushi.
Did you know?
Barbituric acid, the base material of barbiturates, was first synthesized in 1863 by Adolph von Bayer. His company later went on to synthesize aspirin for the first time, and Bayer aspirin is still a popular brand today.
Did you know?
The average office desk has 400 times more bacteria on it than a toilet.
Did you know?
There are more bacteria in your mouth than there are people in the world.