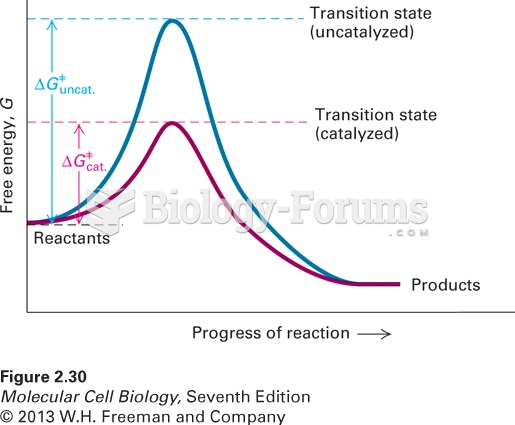
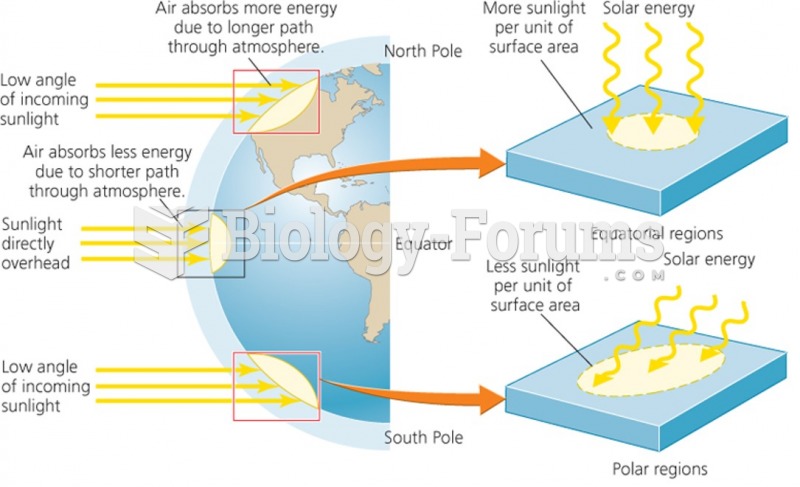
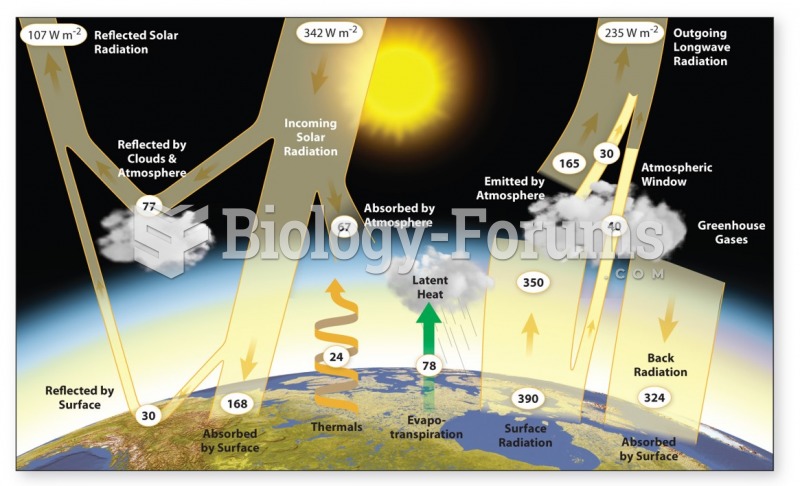
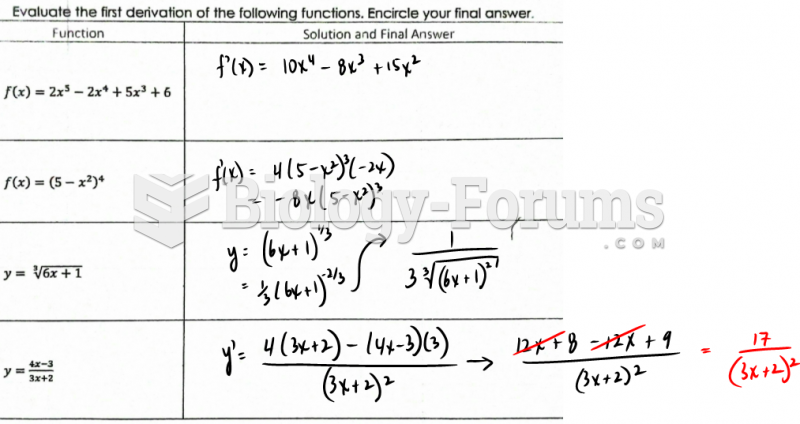
This topic contains a solution. Click here to go to the answer
|
|
|
Did you know?
Oliver Wendell Holmes is credited with introducing the words "anesthesia" and "anesthetic" into the English language in 1846.
Did you know?
Approximately 25% of all reported medication errors result from some kind of name confusion.
Did you know?
Vaccines prevent between 2.5 and 4 million deaths every year.
Did you know?
Most childhood vaccines are 90–99% effective in preventing disease. Side effects are rarely serious.
Did you know?
The average person is easily confused by the terms pharmaceutics and pharmacology, thinking they are one and the same. Whereas pharmaceutics is the science of preparing and dispensing drugs (otherwise known as the science of pharmacy), pharmacology is the study of medications.