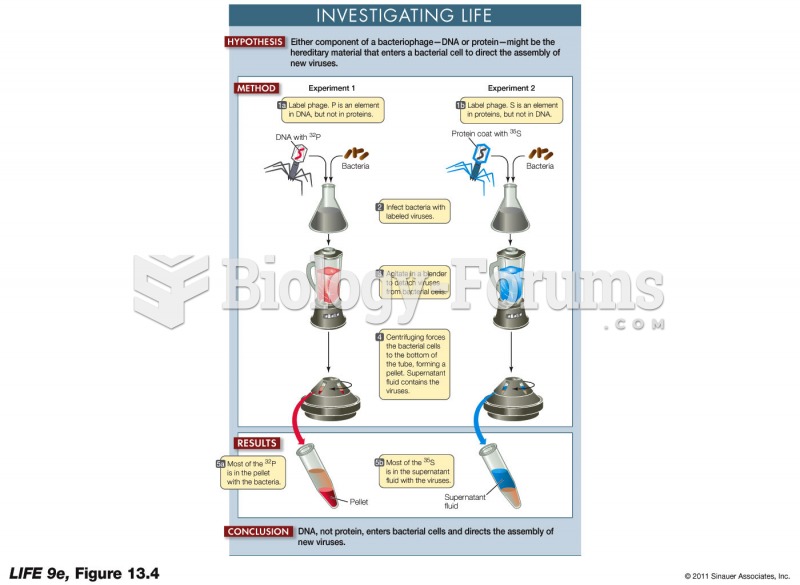
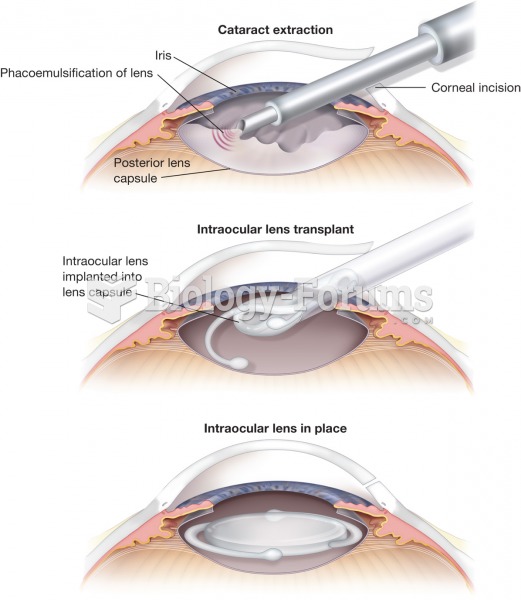
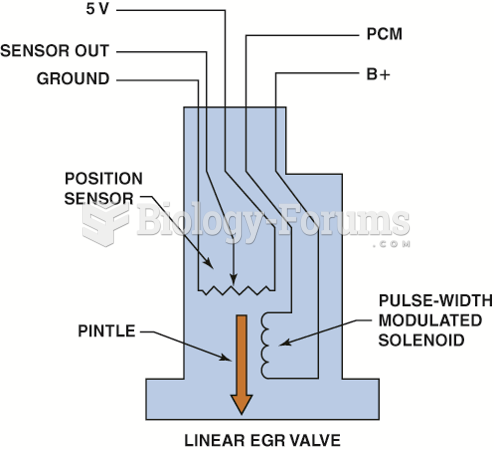
|
|
|
Serum cholesterol testing in adults is recommended every 1 to 5 years. People with diabetes and a family history of high cholesterol should be tested even more frequently.
Malaria was not eliminated in the United States until 1951. The term eliminated means that no new cases arise in a country for 3 years.
The modern decimal position system was the invention of the Hindus (around 800 AD), involving the placing of numerals to indicate their value (units, tens, hundreds, and so on).
According to research, pregnant women tend to eat more if carrying a baby boy. Male fetuses may secrete a chemical that stimulates their mothers to step up her energy intake.
According to the CDC, approximately 31.7% of the U.S. population has high low-density lipoprotein (LDL) or "bad cholesterol" levels.