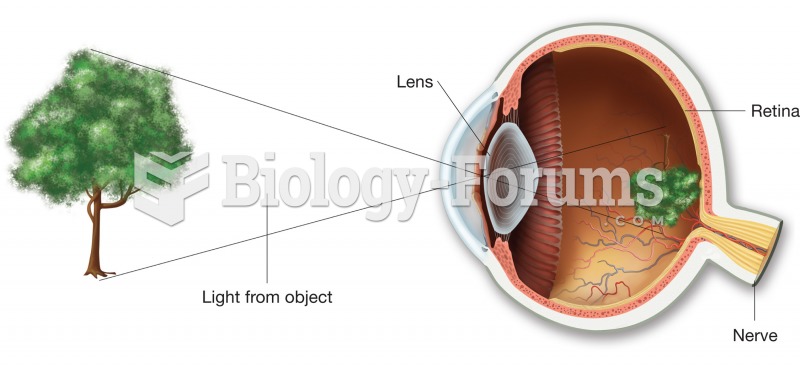
|
|
|
Individuals are never “cured” of addictions. Instead, they learn how to manage their disease to lead healthy, balanced lives.
Interferon was scarce and expensive until 1980, when the interferon gene was inserted into bacteria using recombinant DNA technology, allowing for mass cultivation and purification from bacterial cultures.
Many of the drugs used by neuroscientists are derived from toxic plants and venomous animals (such as snakes, spiders, snails, and puffer fish).
Asthma-like symptoms were first recorded about 3,500 years ago in Egypt. The first manuscript specifically written about asthma was in the year 1190, describing a condition characterized by sudden breathlessness. The treatments listed in this manuscript include chicken soup, herbs, and sexual abstinence.
The familiar sounds of your heart are made by the heart's valves as they open and close.