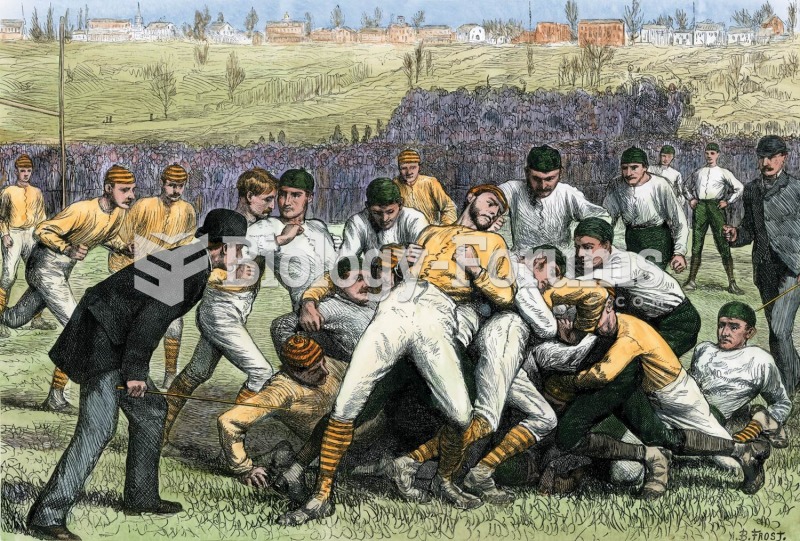
|
|
|
Historic treatments for rheumatoid arthritis have included gold salts, acupuncture, a diet consisting of apples or rhubarb, nutmeg, nettles, bee venom, bracelets made of copper, prayer, rest, tooth extractions, fasting, honey, vitamins, insulin, snow collected on Christmas, magnets, and electric convulsion therapy.
About 60% of newborn infants in the United States are jaundiced; that is, they look yellow. Kernicterus is a form of brain damage caused by excessive jaundice. When babies begin to be affected by excessive jaundice and begin to have brain damage, they become excessively lethargic.
Limit intake of red meat and dairy products made with whole milk. Choose skim milk, low-fat or fat-free dairy products. Limit fried food. Use healthy oils when cooking.
The U.S. Pharmacopeia Medication Errors Reporting Program states that approximately 50% of all medication errors involve insulin.
Despite claims by manufacturers, the supplement known as Ginkgo biloba was shown in a study of more than 3,000 participants to be ineffective in reducing development of dementia and Alzheimer’s disease in older people.