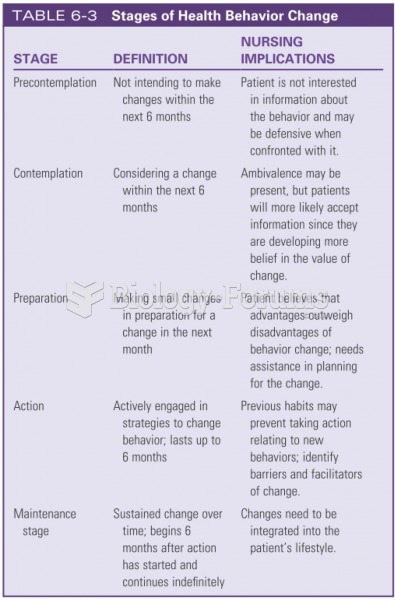
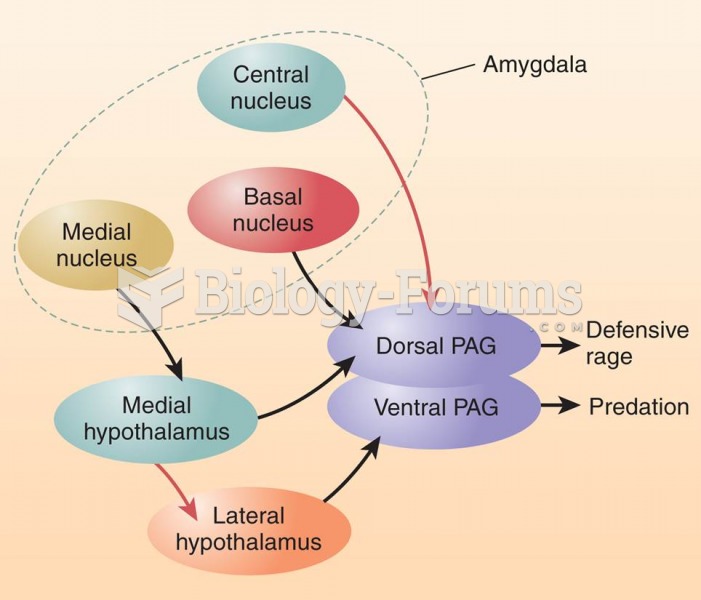
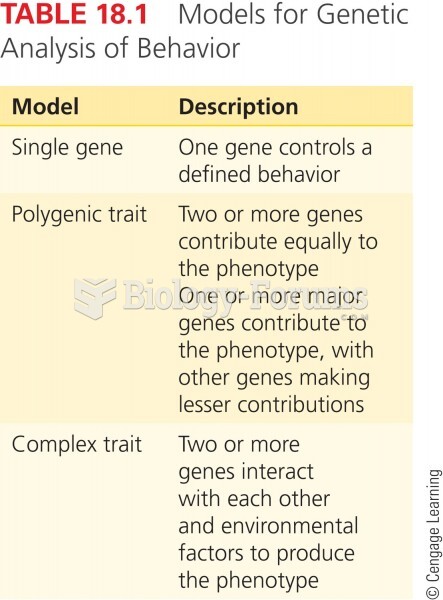
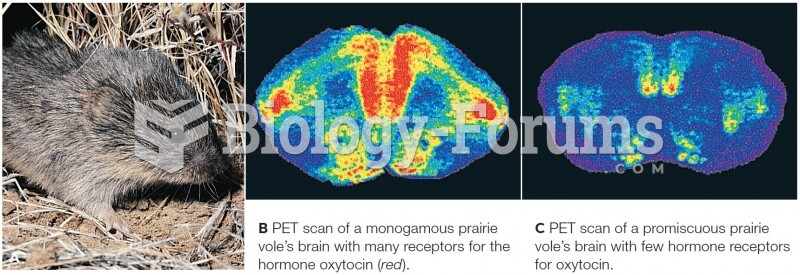
|
|
|
If you use artificial sweeteners, such as cyclamates, your eyes may be more sensitive to light. Other factors that will make your eyes more sensitive to light include use of antibiotics, oral contraceptives, hypertension medications, diuretics, and antidiabetic medications.
The first documented use of surgical anesthesia in the United States was in Connecticut in 1844.
There are 60,000 miles of blood vessels in every adult human.
Human neurons are so small that they require a microscope in order to be seen. However, some neurons can be up to 3 feet long, such as those that extend from the spinal cord to the toes.
Certain topical medications such as clotrimazole and betamethasone are not approved for use in children younger than 12 years of age. They must be used very cautiously, as directed by a doctor, to treat any child. Children have a much greater response to topical steroid medications.