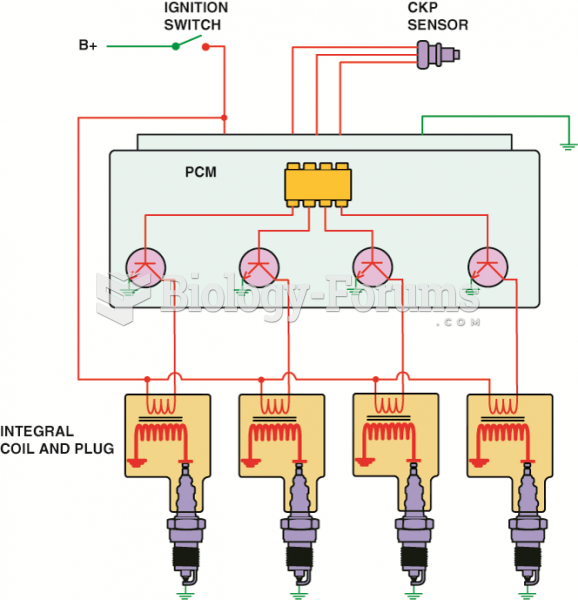
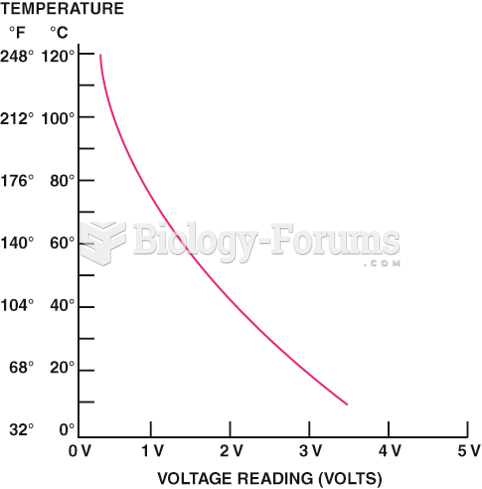
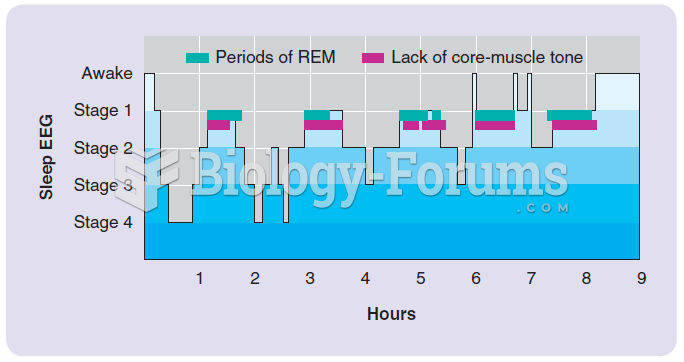
|
|
|
Adults are resistant to the bacterium that causes Botulism. These bacteria thrive in honey – therefore, honey should never be given to infants since their immune systems are not yet resistant.
A serious new warning has been established for pregnant women against taking ACE inhibitors during pregnancy. In the study, the risk of major birth defects in children whose mothers took ACE inhibitors during the first trimester was nearly three times higher than in children whose mothers didn't take ACE inhibitors. Physicians can prescribe alternative medications for pregnant women who have symptoms of high blood pressure.
Approximately one in four people diagnosed with diabetes will develop foot problems. Of these, about one-third will require lower extremity amputation.
Vaccines cause herd immunity. If the majority of people in a community have been vaccinated against a disease, an unvaccinated person is less likely to get the disease since others are less likely to become sick from it and spread the disease.
Walt Disney helped combat malaria by making an animated film in 1943 called The Winged Scourge. This short film starred the seven dwarfs and taught children that mosquitos transmit malaria, which is a very bad disease. It advocated the killing of mosquitos to stop the disease.