|
|
|
Malaria mortality rates are falling. Increased malaria prevention and control measures have greatly improved these rates. Since 2000, malaria mortality rates have fallen globally by 60% among all age groups, and by 65% among children under age 5.
Excessive alcohol use costs the country approximately $235 billion every year.
Dogs have been used in studies to detect various cancers in human subjects. They have been trained to sniff breath samples from humans that were collected by having them breathe into special tubes. These people included 55 lung cancer patients, 31 breast cancer patients, and 83 cancer-free patients. The dogs detected 54 of the 55 lung cancer patients as having cancer, detected 28 of the 31 breast cancer patients, and gave only three false-positive results (detecting cancer in people who didn't have it).
Illicit drug use costs the United States approximately $181 billion every year.
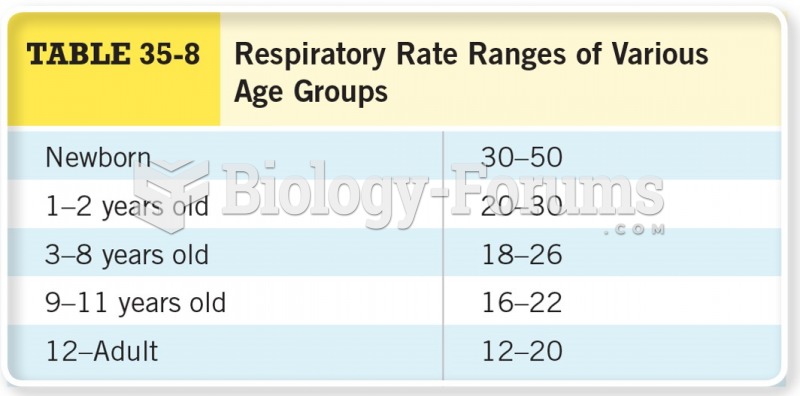
Vital signs (blood pressure, temperature, pulse rate, respiration rate) should be taken before any drug administration. Patients should be informed not to use tobacco or caffeine at least 30 minutes before their appointment.