|
|
|
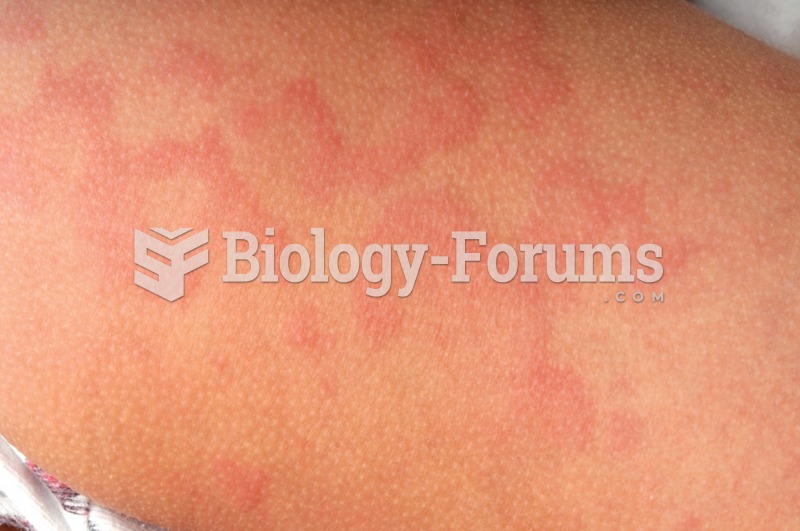
Did you know?
Drying your hands with a paper towel will reduce the bacterial count on your hands by 45–60%.
Did you know?
The familiar sounds of your heart are made by the heart's valves as they open and close.
Did you know?
HIV testing reach is still limited. An estimated 40% of people with HIV (more than 14 million) remain undiagnosed and do not know their infection status.
Did you know?
Symptoms of kidney problems include a loss of appetite, back pain (which may be sudden and intense), chills, abdominal pain, fluid retention, nausea, the urge to urinate, vomiting, and fever.
Did you know?
The longest a person has survived after a heart transplant is 24 years.